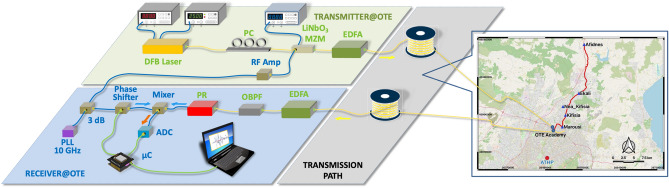
Figure 1.
The experimental setup/conceptual scheme of MFFI: The experimental testbed was installed at OTE Academy. The transmitter consists of a distributed feedback (DFB) laser followed by a polarization controller and a Mach–Zehnder modulator of 10 GHz bandwidth, driven by a 10 GHz tone. An erbium doped fiber amplifier (EDFA) is used to boost the transmitted power. Light propagates from OTE Academy following the path to Marousi–Kifisia–Nea Kifisia–Ekali–Afidnes and vice versa (closed loop) entering the receiver’s EDFA at OTE Academy after approximately 50 km of transmission which translate to 25 dB of losses due to inefficient connections along the link that were inserted in order to emulate a longer link (125 km). The received signal, after optical amplification and proper optical filtering with the use of an optical band-pass filter (OBPF) for the reduction of amplifier’s noise is photodetected and mixed with the transmitter’s signal in order to extract the phase noise attributed to optical transmission. The baseband signal of phase noise is digitized with the use of an analog to digital converter and processed by a computer (see methods). Fiber deformations due to seismic events are imprinted on the phase noise. The map has been created using open software QGIS ver 3.16LTR (https://www.qgis.org/en/site/index.html).