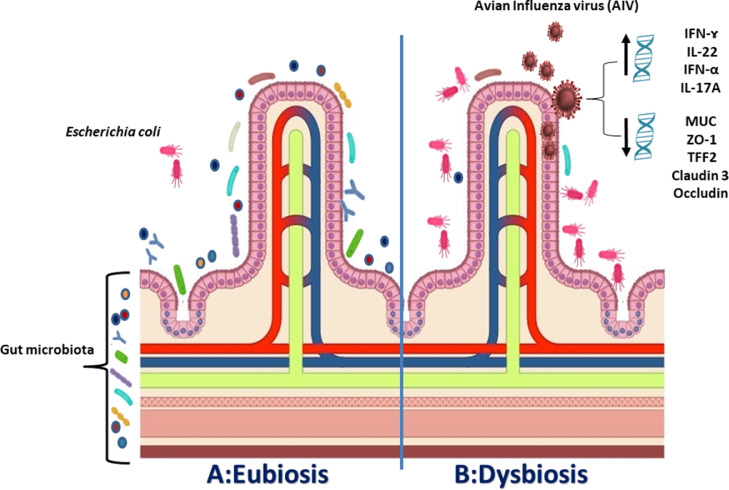
Figure 4.
(A) Eubiosis; a sort of balanced environment “Eco-system” express the presence of different types of gut microbiota together providing intestinal integrity and limiting the attachment of pathogenic pathogens as Escherichia coli. (B) Dysbiosis; explain that during the infection with AIV, the number of gut microbiota is significantly decreased while the number of secondary pathogenic bacteria increased. Furthermore, genes expression for proinflammatory cytokines IFN-ɤ, IFN-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-22, and IL-17A were significantly increased while, genes expression for MUC, ZO-1, Claudin 3, Occludin, TFF2, and Muc2 (responsible for intestinal mucin layer and intestinal mucosa healthiness) were significantly decreased resulting in an eruption of intestinal mucosa enabling secondary infection with E. coli which may lead to systemic infection.