Figure 5.
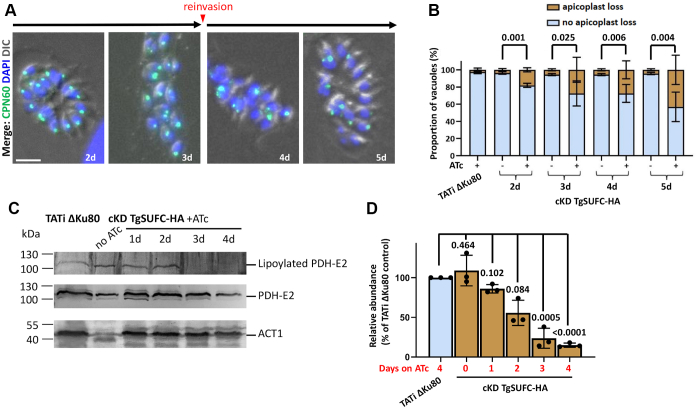
TgSUFC depletion impacts apicoplast-hosted Fe-S pathways.A, cKD TgSUFC-HA parasites were kept in the presence of ATc for up to 5 days, and the aspect of the apicoplast was evaluated by microscopic observation using the specific CPN60 marker. After 3 days, parasites egressed and were used to reinvade new host cells for subsequent timepoints. The scale bar represents 5 μm. DNA was labeled with DAPI. B, using the labeling described in (A), apicoplast loss in vacuoles was monitored after 2 to 5 days of incubation with ATc. At least 50 vacuoles were assessed per condition, and the percentage of vacuoles presenting less apicoplasts than the total number of parasites was recorded (reflecting at least a partial apicoplast loss within the vacuole). Data are mean values from n = 3 independent experiments ±SD. Two-tailed Student’s t test p-values are indicated. C, a decrease in the lipoylation of the E2 subunit of pyruvate dehydrogenase (TgPDH-E2), which depends on the apicoplast-hosted Fe-S–containing lipoyl synthase LipA, was observed by immunoblot using an antilipoic acid antibody on cell extracts from cKD TgSUFC-HA parasites kept with ATc for an increasing period of time. A polyclonal antibody raised against PDH-E2 was used as a control for global abundance of the protein and for apicoplast integrity. TgACT1 was used as a loading control. D, decrease of lipoylated TgPDH-E2 was quantified by band densitometry and normalized with the internal loading control. Data represented are mean ±SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Two-tailed Student’s t test p-values are indicated. DIC, differential interference contrast; Fe-S, iron-sulfur; HA, hemagglutinin; ATc, anhydrotetracycline; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; DAPI, 4,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; cKD, conditional knockdown; LipA, lipoyl synthase.