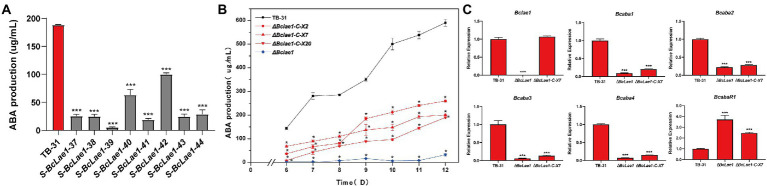
Figure 1.
Deletion of Bclae1 affects ABA synthesis. (A) Eight Bclae1 gene silencing strains were randomly selected to grow on PDA. Samples for the quantitative determination of ABA production were collected at day 7. The error bars indicate the standard errors of the mean (SEM) for three replicate cultures (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences in ABA production between selected silencing mutants and TB-31 (p < 0.001). (B) The ΔBclae1 mutant and three randomly selected ΔBclae1-C mutants (ΔBclae1-C-X2, ΔBclae1-C-X7, ΔBclae1-C-X20) were grown on PDA. Samples for the quantitative determination of ABA production were collected at 6–12 days. The error bars indicate the standard errors of the mean for three replicate cultures (n = 3). Asterisks indicate significant differences in ABA production between selected mutants and TB-31 (p < 0.05). (C) RT-qPCR examining the transcriptional levels of ABA gene cluster, BcabaR1 and Bclae1 in ΔBclae1 mutant, ΔBclae1-C-X7, and TB-31. The relative transcriptional levels of selected genes were obtained after normalization to the constitutive tubulin reference gene (BC1G_05600) at 6 days. The relative values for selected genes transcription at 6 days in TB-31 were arbitrarily assigned as 100%. Shown are means and SEM, n = 3 independent biological replicates. ***p < 0.001 versus the same genes of the TB-31 group.