Figure 1. Schematic of a GelMA-AlgMA hybrid hydrogel undergoing photo/ionic crosslinking and tissue adhesion.
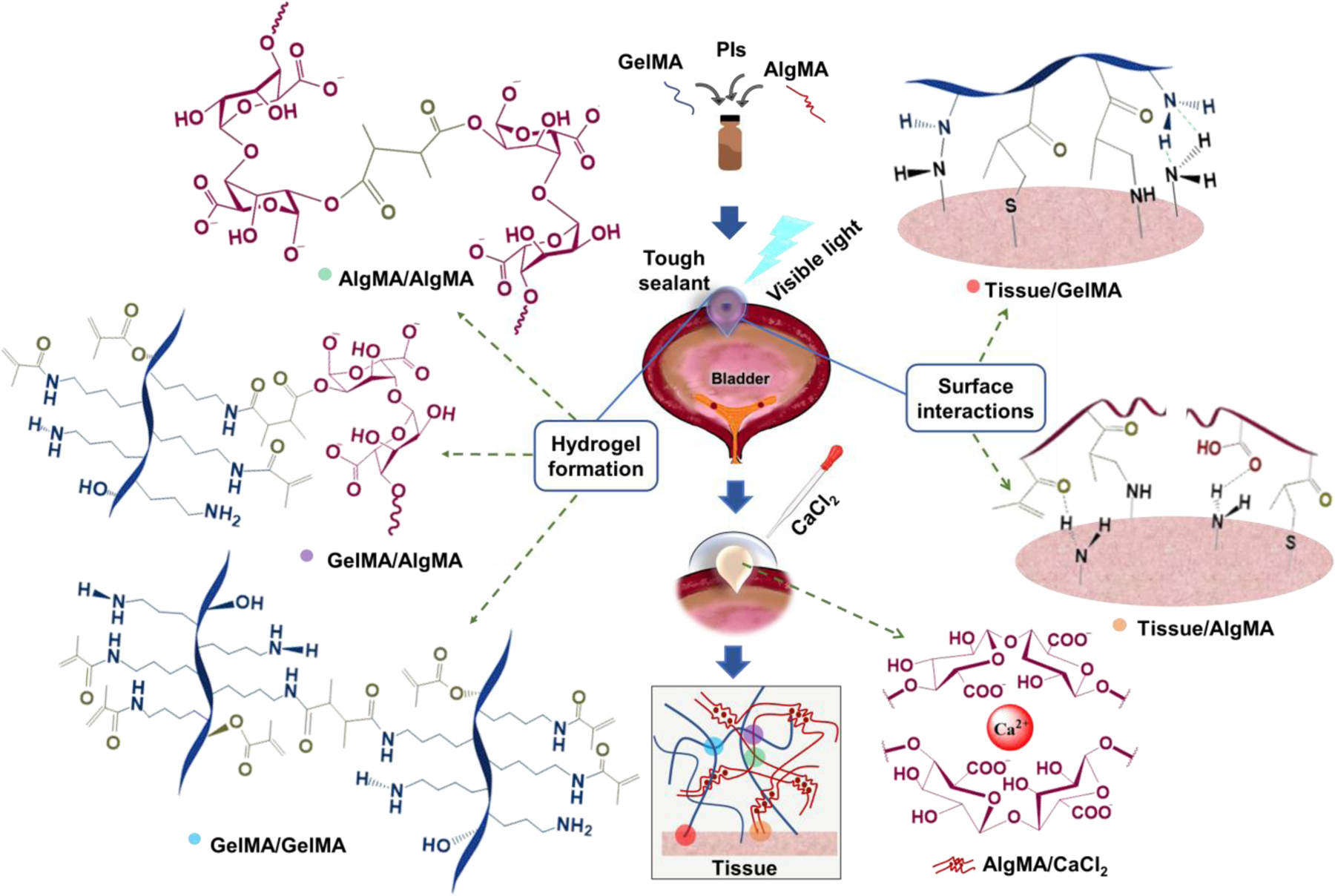
Both AlgMA and GelMA undergo covalent crosslinking through the photo-initiated polymerization of methacrylate/methacryloyl (MA) groups. In AlgMA, the G blocks on the polymer chains form ionic bonds with Ca2+, providing a reversibly crosslinked network. Crosslinking hybrid GelMA/AlgMA hydrogels yields two types of polymer networks intertwined and connected by covalent bonds (via MA groups) supplemented by the Ca2+-mediated physical bonds of AlgMA. GelMA may interact with amine-rich biological tissues through the formation of hydrogen bonds as well as covalent bonding of amine-MA and thiol-MA groups. AlgMA can interact with the tissue via hydrogen bonding, covalent bonding, and/or electrostatic interactions between the carboxylate and amino groups.
