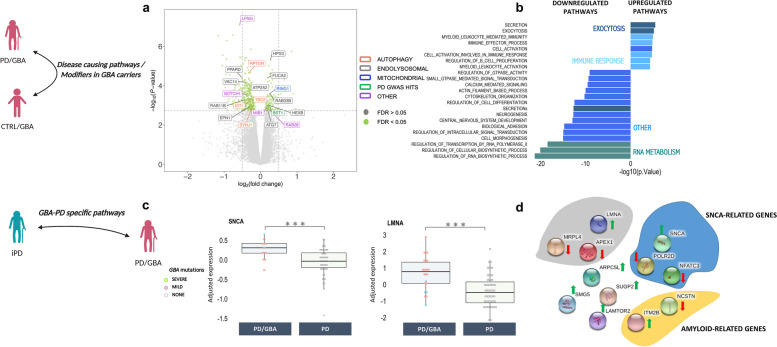
Fig. 2.
Differential expression profiles between PD/GBA, CTRL/GBA, and PD. a-b PD/GBA vs CTRL/GBA. a Volcano plot represents log2 fold change (log2FC) (x-axis) and -log10 of P-values (y-axis) of the differentially expressed genes between PD/GBA and CTRL/GBA groups. Green dots represent genes with FDR < 0.05. Selected genes were highlighted based on overlap targeted pathways as indicated in the legend on the right side. b Pathway enrichment analysis of differentially expressed genes between PD/GBA vs CTRL/GBA subjects. Pathway enrichment of genes differentially expressed between PD/GBA and CTRL/GBA subjects with FDR < 0.05 for GO terms are reported. Light blue: pathways related to the immune response; Dark green: pathways related to exocytosis; Light green: pathways related to RNA metabolism; Dark blue: other pathways. c-d PD/GBA vs PD. c Differential normalized expression count of SNCA and LMNA between PD/GBA and PD. Disease and genetic status are reported on the x-axes. Each dot represents a subject. Dots are colored based on GBA mutations (as reported in the legend: GBA mild mutations (N370S, E326K, R496H), GBA severe mutations (L444P/A456P/RecNciI, V394L, 84GG, 84GG/T369M, N370S/RecNciI)). Asterisks indicate significant adjusted p-value (* = adjusted p-value < 0.05, ** = adjusted p-value < 0.01, *** = adjusted p-value < 0.001; statistics: Mann-Whitney U test). d Schematic representation (STRING, [150]) of functionally relevant genes differentially expressed between PD/GBA and PD cohorts. Genes are grouped in colored circles based on shared functional pathways (yellow: amyloid-related genes, blue: SNCA-related genes, grey: PD hits related genes). Arrows indicate whether genes are up (green) or down (red) regulated in the PD/GBA vs the PD cohort