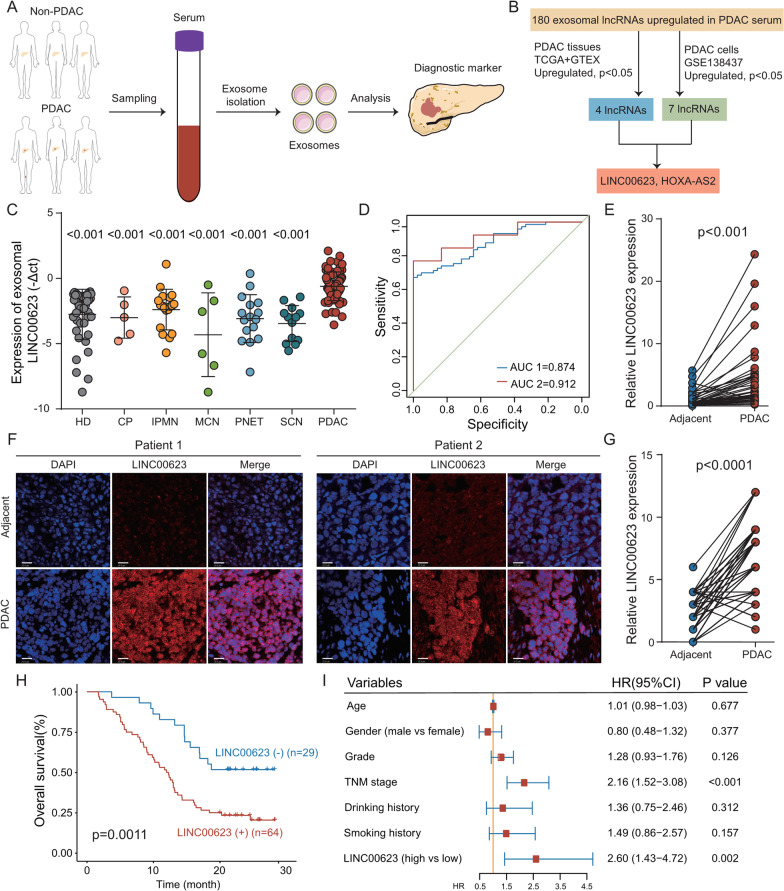
Fig. 1.
Exosomal LINC00623 is upregulated in PDAC and has clinical significance. a Workflow of screening for exosomal diagnostic biomarkers in the serum of patients with PDAC and healthy individuals. b Flowchart showing the process used to narrow down the upregulated exosomal lncRNAs in the serum of patients with PDAC compared to that of healthy individuals. c The levels of circulating exosomal LINC00623 were significantly higher in patients with PDAC than in healthy donors (HD) and patients with benign pancreatic neoplasms. Chronic pancreatitis (CP), intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm (IPMN), mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN), pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor (PNET), serous cystic neoplasm (SCN). Independent Student’s t test, P < 0.001. d Diagnostic AUC value of the circulating exosomal LINC00623 level. AUC1: PDAC (n = 73) vs. HD (n = 42); AUC2: PDAC with normal CA19-9 levels (n = 13) vs. HD (n = 42). e Relative expression of LINC00623 as measured by RT-qPCR in PDAC and matched adjacent normal tissues (n = 40). Independent Student’s t test, P < 0.001. f Representative images of FISH of LINC00623 (red) in 93 pairs of PDAC and adjacent normal tissues. DAPI (blue) was used for nuclear counterstaining. Scale bar = 20 μm. g The expression level of LINC00623 as determined by FISH in PDAC and adjacent normal tissues (n = 93). Independent Student’s t test, P < 0.001. h Kaplan‒Meier survival curve of two groups of patients with PDAC (n = 93): LINC00623(+), patients with high LINC00623 expression; LINC00623(−), patients with low LINC00623 expression. The expression of LINC00623 was determined by FISH. i Univariate Cox regression analyses of the survival of patients with PDAC (n = 93)