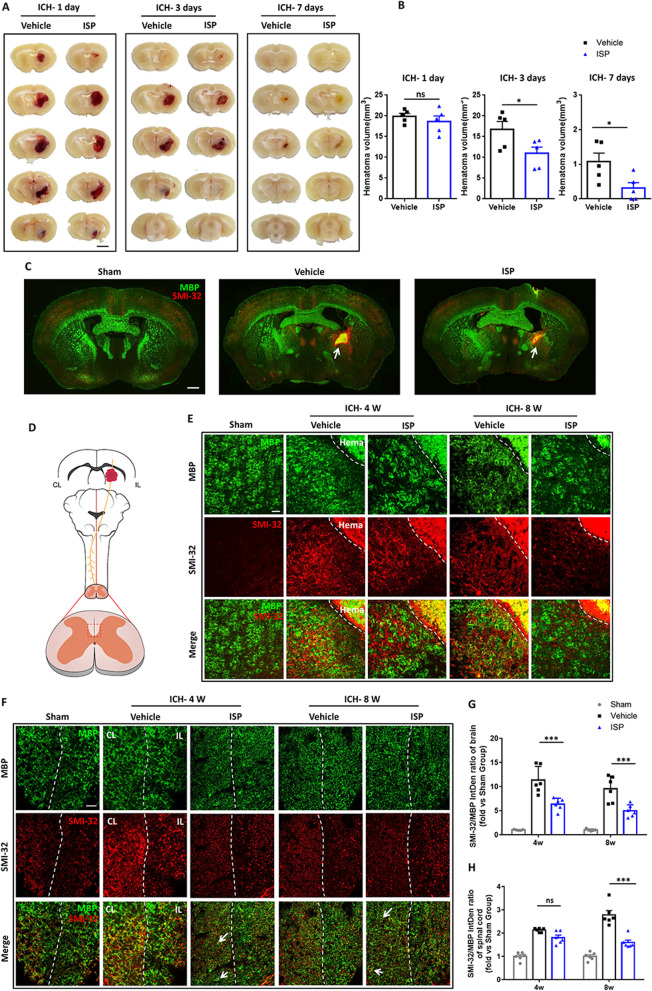
Fig. 4.
ISP treatment improves long-term brain and cervical spinal cord white matter after ICH. a Representative serial coronal brain sections showing the volume of red-hued hematoma in ISP-treated mice were significant smaller than vehicle-treated mice at days 1, 3 and 7 after ICH. Scale bar, 2.5 mm. b Quantification of hematoma volumes was based on photographs of consecutive brain sections taken at days 1, 3 and 7 after ICH. c Representative coronal sections were stained with MBP and SMI-32 at week 4 post-ICH. White arrow indicates the hematoma in vehicle and ISP groups. Scale bar, 600 µm. d Schematic diagram shows that ICH included white matter injury of dorsal spinal cord on the contralateral CST side. e, g Images of MBP (green) and SMI-32 (red) immunostaining in brain around the hematoma in all groups at weeks 4 and 8 after ICH. Scale bar, 50 µm. Statistical analysis shows a significant reduction in the SMI-32/MBP intensity ratio in the ISP group compared to the vehicle group at weeks 4 and 8. f, h Images of MBP (green) and SMI-32 (red) immunostaining of contralateral CST in transverse cervical spinal cord sections in three groups at weeks 4 and 8 after ICH. White arrow indicates axons (red) enwrapped by myelin sheath (green). Scale bar, 20 µm. Compared to vehicle treatment, ISP application decreased the SMI-32/MBP intensity ratio of CST at weeks 4 and 8. n = 5–6 per group. Data were analyzed by unpaired Student t test between two groups and one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test between three groups, and expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ns not significant