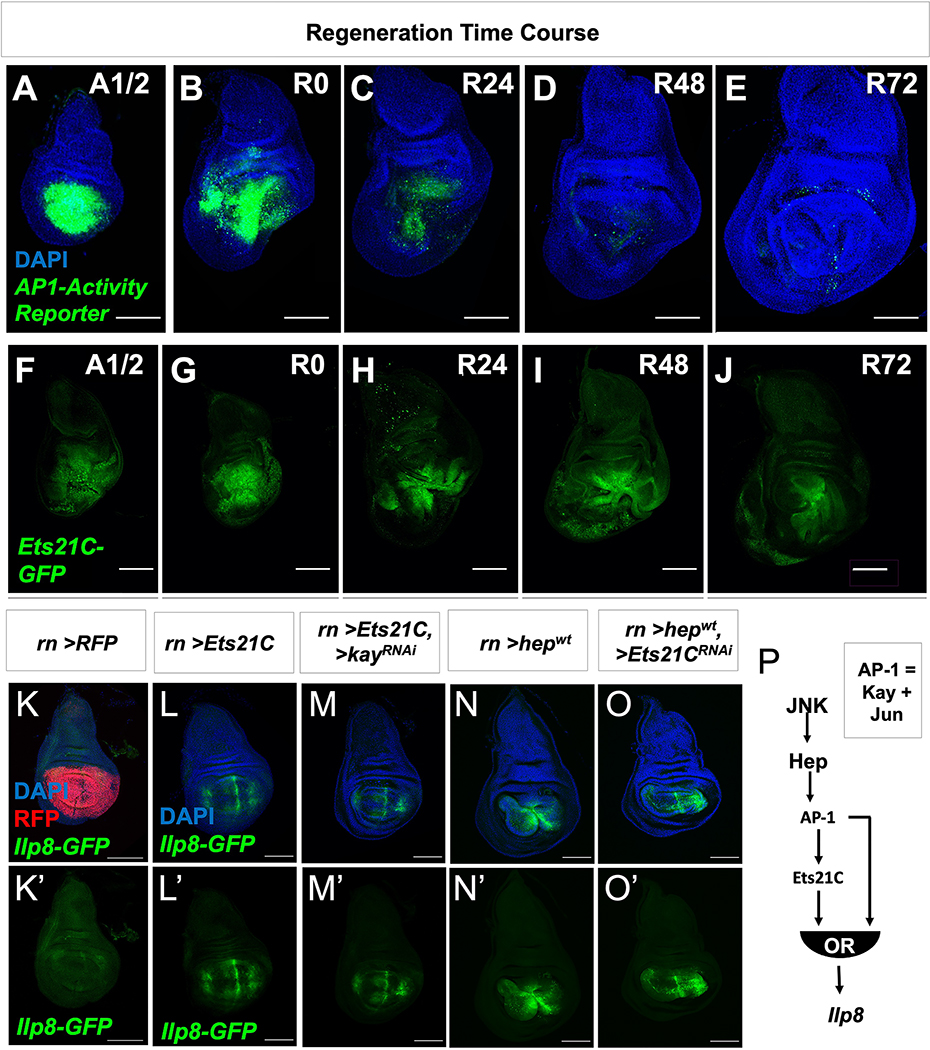
Figure 6. JNK/AP-1 and Ets21C form a feed-forward loop to sustain target gene expression.
(A-E) Expression of AP-1-activity reporter (AP-1-GFP) and (F-J) Ets21C-GFP over the course of regeneration. Wing imaginal discs were dissected half-way (20 h) through the ablation period (A1/2) and at time points after the downshift to 18°C (indicated in hours) during regeneration (R0, R24, R48, R72). Regeneration is near complete by 72 h. (K-O) The pouch driver rotund (rn-GAL4) was used to drive the overexpression of (K) UAS-RFP, (L) UAS-Ets21C, (M) UAS-Ets21C together with UAS-kayak-RNAi (kayak (kay) encodes for one component of the AP-1 complex), (N) UAS-hepwt (upstream activating kinase of AP-1), and (O) UAS-hepwt together with UAS-Ets21C-RNAi. Note that all conditions besides the control (UAS-RFP) resulted in the expression of Ilp8-GFP within the pouch. (P) From these overexpression data, the time course of AP-1 activity and Ets21C expression (A-J), and loss-of-function experiments (Figure 4; Figure S4), we predict that JNK/AP-1 and Ets21C form a type 1 coherent feed-forward loop to control the expression of Ilp8 with either pathway being able to activate expression independently of the other. Microscopy scale bars = 100 μm. See also Figure S6.