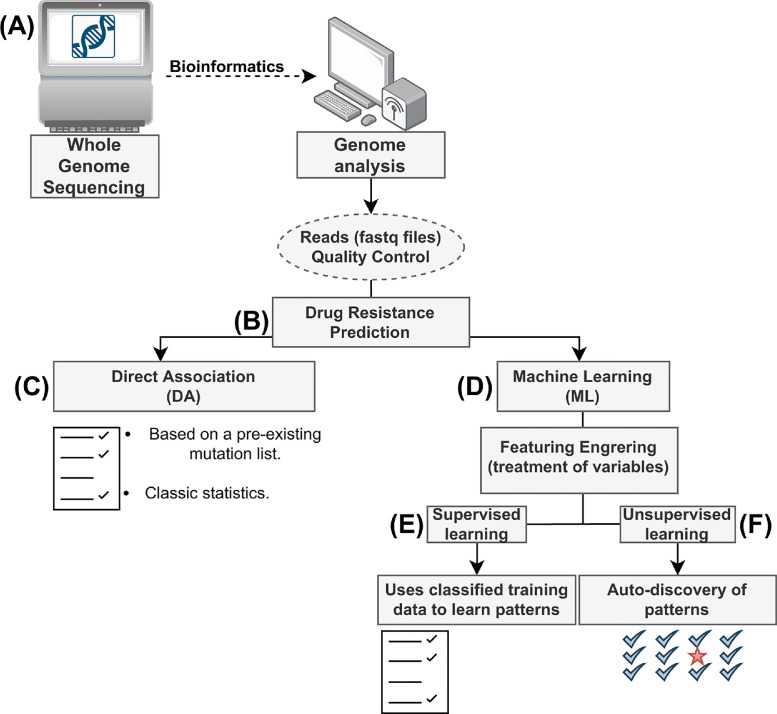
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram for prediction of drug resistance from whole genome sequencing (WGS) data using computational approaches. (A) The data generated from WGS (FASTQ files) for (B) predicting drug resistance either using (C) the classical Direct Association, which relies on a database of documented mutations at present or (D) Machine learning techniques, such as (E) Supervised Learning, which relies on guided training of algorithms on hand-curated data to predict the effects of novel mutations or (F) Unsupervised Learning, which relies on algorithmic techniques to discover patterns and predict effects of the mutations.