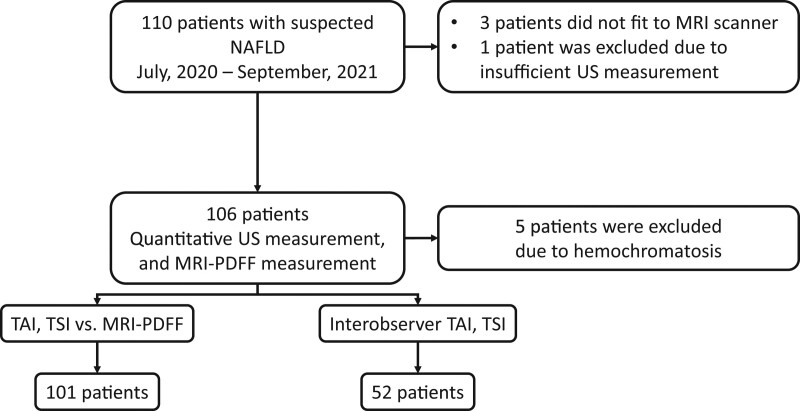
Figure 1.
Patient selection and study design. We enrolled 110 participants with suspected NAFLD into this prospective study. One hundred six patients with suspected liver steatosis who fulfilled the inclusion criteria underwent both quantitative ultrasound and MRI-PDFF measurements to determine the liver’s fat content. Three morbidly obese patients had been excluded because they did not fit into the MRI scanner, an additional patient was excluded due to failure of the ultrasound measurement, and further 5 patients were excluded due to hemochromatosis, which can interfere with MRI-PDFF. The final patient cohort included 101 NAFLD patients. In 52 cases, 2 examiners independent from each other performed quantitative ultrasound measurements to assess the interobserver reproducibility of TAI and TSI values. MRI-PDFF = magnetic resonance imaging-based proton density fat fraction measurement, NAFLD = nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, TAI = tissue attenuation imaging, TSI = tissue scatter distribution imaging.