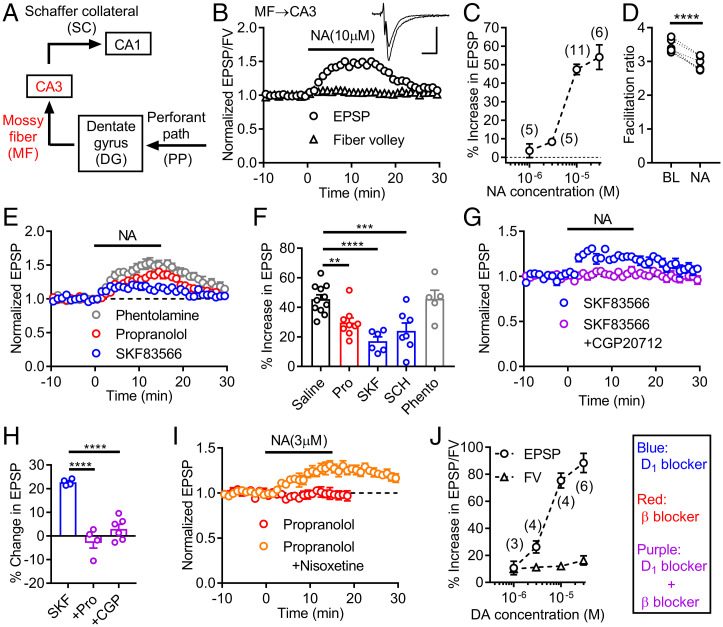
Fig. 1.
Activation of D1 receptors by noradrenaline potentiates mossy fiber synaptic transmission in the hippocampus. (A) Schematic diagram of hippocampal excitatory circuit highlighting mossy fiber (MF)–CA3 connection. (B) Effects of noradrenaline (NA) applied at the bar on presynaptic fiber volley (FV) and EPSPs at MF–CA3 synapse. Sample traces show averaged field potentials before and during NA application (scale bars: 10 ms, 0.2 mV). (C) Dependence of synaptic potentiation on NA concentrations. (D) Decrease in triple-pulse facilitation at 200-ms intervals by NA. BL: baseline. Paired t test (t5 = 11.77, ****P < 0.0001). (E) NA-induced synaptic potentiation in D1 antagonist SKF83566 (SKF) (200 nM), β antagonist propranolol (Pro) (10 μM) or α antagonist phentolamine (Phento) (20 μM). (F) Summary of antagonist effects on NA-induced synaptic potentiation. SCH: SCH23390 (D1 antagonist, 50 nM). One-way ANOVA (F4,33 = 10.2, P < 0.0001) followed by Dunnett's test (**P = 0.0085, ***P = 0.0009, ****P = 0.0001). (G) Block of SKF-resistant potentiation by β1 antagonist CGP20712 (CGP) (100 nM). (H) Summary of β antagonist effects on SKF-resistant potentiation. One-way ANOVA (F2,11 = 35.66, P < 0.0001) followed by Dunnett's test (****P = 0.0001). (I) D1-receptor–dependent synaptic potentiation by low micromolar NA in presence (n = 6) and absence (n = 3) of nisoxetine (1 μM). (J) Dependence of FV and EPSP potentiation on dopamine (DA) concentrations. The number of data is shown in the graph in C and J. Data are presented as means ± SEM in all figures with or without individual values.