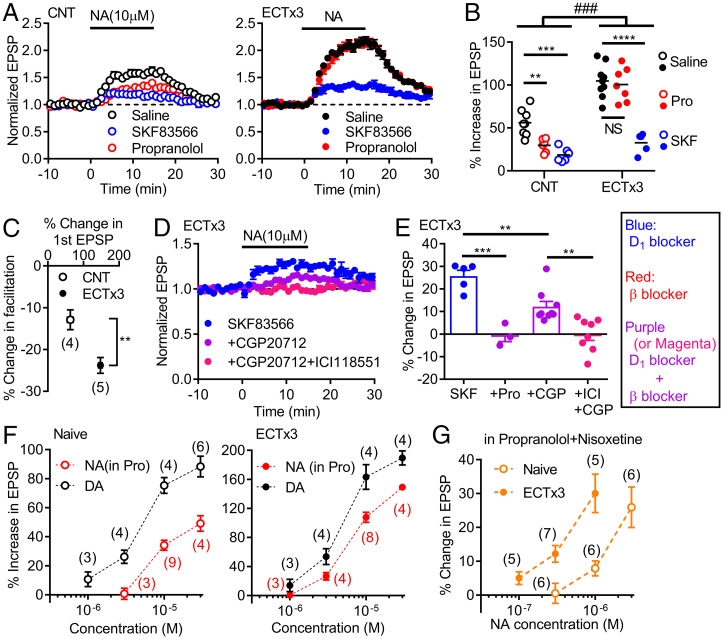
Fig. 3.
Activity-dependent enhancement of noradrenaline–D1 receptor signaling. (A) Effects of NA in control mice (CNT) and mice treated with three times of ECT (ECTx3) in normal saline or in antagonists. (B) Summary of data shown in A. Two-way ANOVA (ECT effect, F1,35 = 83.22, P < 0.0001; drug effect, F2,35 = 42.98, P < 0.0001; interaction, F2,35 = 10.13, ###P = 0.0003) followed by Tukey's test (NS: not significant, **P = 0.0083, ***P = 0.0002, ****P < 0.0001). (C) Effects of ECTx3 on reduction of triple-pulse facilitation by NA (t7 = 3.644, **P = 0.082). (D) Effects of β receptor antagonists on SKF-resistant component of NA-induced potentiation in ECT-treated mice. (E) Summary of β antagonist effects on SKF-resistant component of NA-induced potentiation. CGP (100–200 nM), ICI: ICI118551 (β2 antagonist, 100–200 nM). One-way ANOVA (F3,21 = 17.37, P < 0.0001) followed by Bonferroni's test (**P < 0.01, ***P = 0.0001). (F) Dependence of D1-mediated synaptic potentiation on NA and DA concentrations in naive and ECT-treated mice. The DA data in naive mice are the same as those in Fig. 1J. (G) Dependence of D1-mediated potentiation on NA concentrations in nisoxetine. The number of data is shown in the graph in C, F, and G.