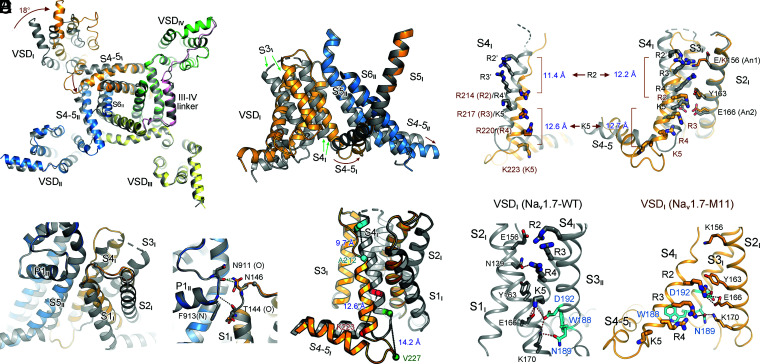
Fig. 2.
Multimodal conformational changes of VSDI between its up and down states. (A) Large-degree conformational changes between M11 and WT mainly occur in repeats I and II. (Left) An intracellular view of the superimposed α subunits from M11 (domain colored) and WT (dark gray). Intracellular segments are omitted for visual clarity. (Right) A side view of the rotation of VSDI and the ensuing S4-5I segment. Brown arrows indicate the shift of the corresponding segments from WT to M11. (B) The pivot for VSDI rotation. VSDI swings around the contact between the extracellular tips of S1I and P1II. (Right) The interactions between the carbonyl oxygen of Thr144 and the side chain of Asn146 in VSDI with main-chain groups of the starting turn of P1II helix are preserved in M11 and WT, representing the pivoting point for VSDI rotation. (C) Dissection of conformational changes of VSDI between the up (WT) and down (M11) states. An enlarged view of the superimposed VSDI and the S4-5I linker from A is shown. Structural shifts of S4I combine helical unwinding, tilted sliding, and axial rotation. Cα atoms of the residues that mark the termini of S4I helices in the two structures are shown as spheres. The linear displacement of the Cα atoms of these residues in the context of overall structural comparison are indicated. S1–S3I segments rotate around S4I. (D) Downward transfer of three GC residues in VSDI from WT to M11. The linear displacement of the Cα atoms of R2 and K5 residues, which mark the two ends, in the context of overall structural comparison (Left) and individual VSDI comparison (Right) are indicated. The WT residues are labeled with apostrophe. (Right) When the structures of VSDI are individually compared, S1–S3 can be completely overlaid. (E) A conserved WNФФD motif on the cytoplasmic terminus of S3I stabilizes the GC residues in the down conformation of VSDI. Ф stands for hydrophobic residues. (Left) Coordination of GC residues in the up VSDI in WT. S1I is omitted for visual clarity. (Right) R2–R4 are stabilized by the WNФФD motif in the down VSDI in M11. The top GC residue R2 forms cation–π interaction with the occluding Tyr163 on S2I and electrostatic interaction with Asp192 in the WNФФD motif. Red and black dashes indicate distances of 2.8 to 3.5 Å and 4.5 to 5.5 Å, respectively.