Fig. 2.
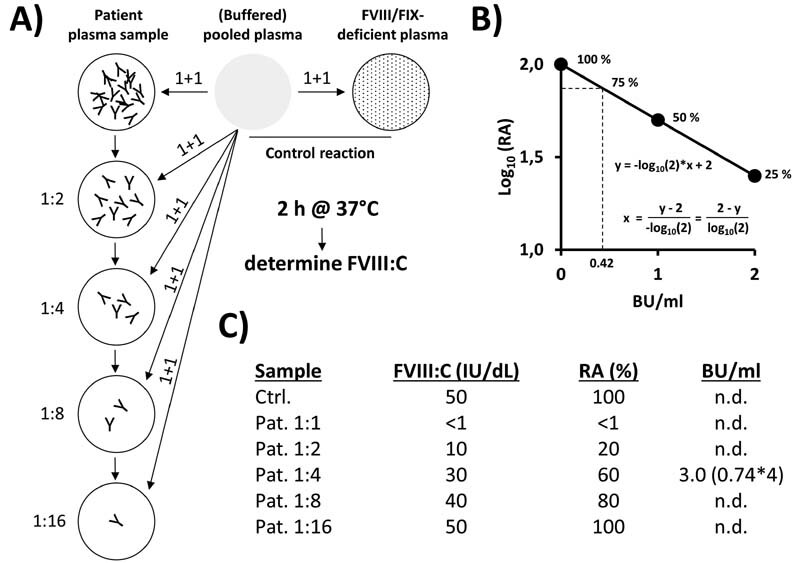
Principle of the (Nijmegen)-Bethesda Assay for quantitative determination of inhibitory antibodies against FVIII or FIX. (A) In an exemplary procedure, a heat-inactivated patient plasma sample with an inhibitor titre of 3 Bethesda units (BU)/mL is serially diluted in the respective factor-deficient plasma (or buffer) and the single dilutions are mixed with equal amounts (1 + 1) of (buffered) pooled plasma ([B]PP). As a control, the (B)PP is mixed 1 + 1 with factor-deficient plasma. After incubation (e.g., 2 hours at 37 °C for FVIII inhibitor testing, no such long incubation required for FIX inhibitor testing), (residual) factor activities are measured and calculated relative (%) to that of the control reaction (relative activities [RA], panel C ). ( B ) Inhibitor titres are usually given as BU/mL according to the definition that one BU/mL inhibits the FVIII/FIX activity by 50% (50% RA) and two BE/mL by further 50% (25% RA). The corresponding ideal interpolation function (including 0 BU/mL = 100% RA) that allows the calculation of BU/mL from determined RA values is shown in the graph (RA [ y -axis, log 10 ] versus BU/mL [ x -axis]). The defined range of valid RAs is limited from 75% down to 25%, necessitating the testing of sample dilutions in case of inhibitor titres of > 2 BU/mL. ( C ) Measured factor activities and calculated RA values for the exemplary inhibitor-positive plasma sample (dilutions). Only the 1:4 dilution shows a RA value (60%) within the defined acceptable range of 25 to 75%. Based on the formula shown in panel B , a BU/mL titre of 0.74 is calculated, corresponding to 3 BU/mL in the original sample after correction for the initial dilution.
