Figure 1.
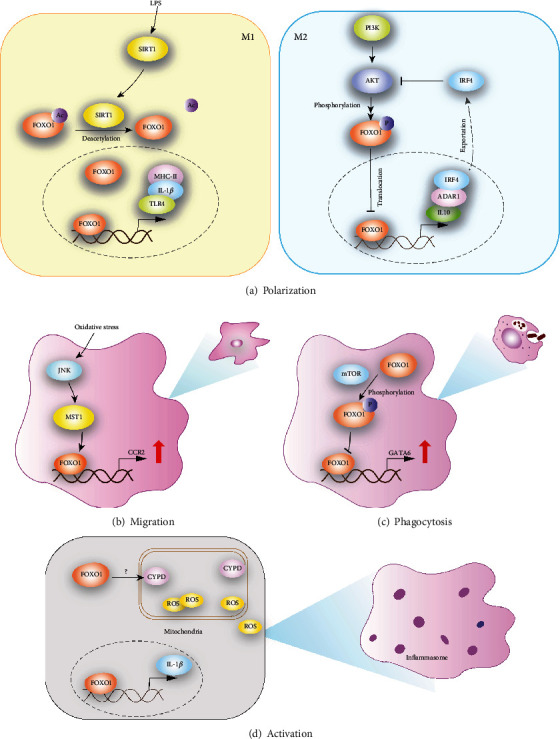
Schematic diagram for the regulatory effect of FoxO1 on macrophage. (a) The role of FoxO1 in macrophage polarization. SIRT1 can promote the deacetylation of FoxO1 in the presence of LPS stimulation, which in turn accelerates nuclear translocation of FoxO1. FoxO1 skews macrophage towards M1 phenotype through binding to the promoter regions of MHCII and IL-1β directly. The other hand, FoxO1 up-regulates the expression of IL-10 and ADAR1, which is critical for M2 induction. FoxO1-driven IRF4 transcription promotes nuclear translocation of FoxO1 mediated by inhibiting PI3K-Akt signaling. (b) The function of FoxO1 in macrophage migration. Under oxidative stress, FoxO1 signaling is enhanced through JNK-MST1 pathway and facilitates CCR2 expression, leading to reinforced macrophage migration. (c) The effect of FoxO1 activity on macrophage phagocytosis. The expression of pro-phagocytotic factor GATA6 is upregulated by nuclear FoxO1, while the phosphorylation of FoxO1 hampers the nuclear translocation of FoxO1 following mTOR activation. (d) The impact of FoxO1 on macrophage inflammasome activation. Upon activation, FoxO1 drives the transcription of IL-1β and accelerates LPS-induced mitochondrial ROS production. FoxO1 also serves as an important link bridging ROS accumulation and inflammasome activation. SIRT1, sirtuin1; ADAR1, adenosine deaminase acting on double-stranded RNA 1; MST1, Mammalian STE20-like kinase-1; CYPD, Cyclophilin D.
