Figure 2.
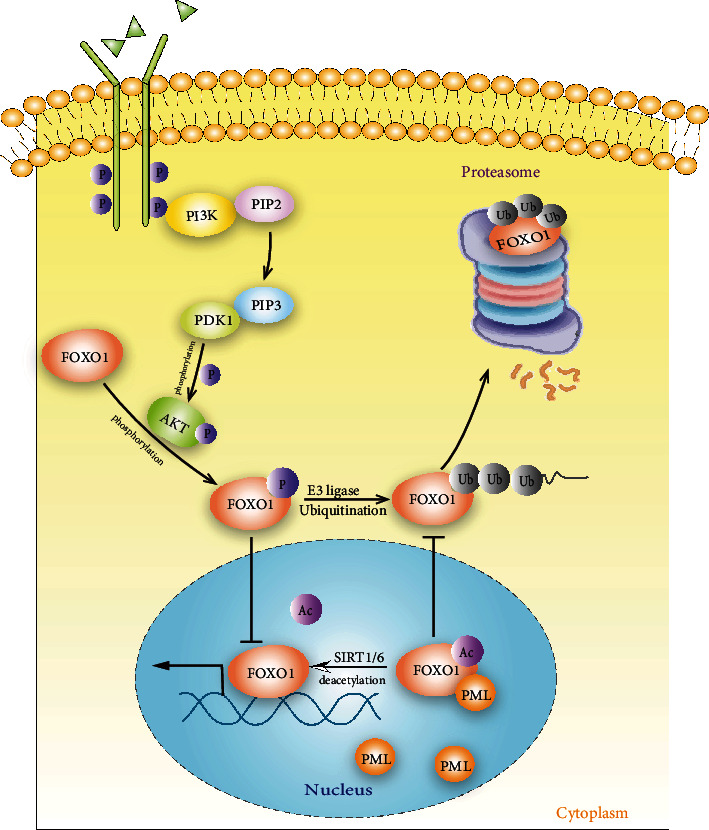
Activity of FoxO1 is under tightly control in macrophage. Protein phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination are the major post-translational modification forms that affect the expression level, subcellular distribution and the transcriptional activity of FoxO1. Phosphorylation, PI3K/AKT signaling pathway mediates the phosphorylation of FoxO1, whereas phosphorylation inhibits its function by promoting the nuclear exportation and subsequent protein degradation; Acetylation, Deacetylation of FoxO1 is essential for its nuclear translocation and functional activity during which process SIRTs are the key regulators in macrophage; Ubiquitination, the degradation of FoxO1 ubiquitination mainly dependents on ubiquitination in macrophages. The phosphorylation combined with acetylation and ubiquitination orchestrates FoxO1 function. The phosphorylation leads to an increased nuclear exportation of FoxO1, the exported FoxO1 is ubiquitinated and subsequently degraded in cytoplasmic proteasomes. On the contrary, the acetylation of FoxO1 fosters the nuclear transcription and negatively regulates the ubiquitination. PML, Promyelocytic Leukemia Nuclear Bodies; SIRT6, sirtuin-6 (NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-6).
