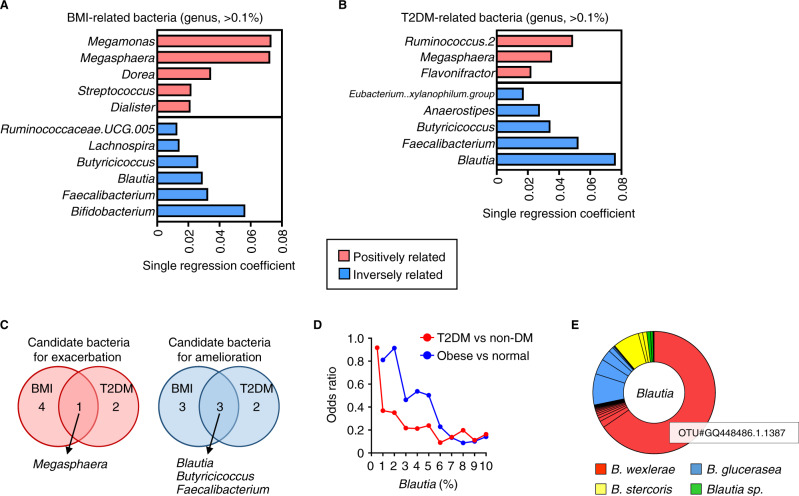
Fig. 1. Intestinal bacterial genera associated with body mass index (BMI) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Japanese adults.
A BMI-related bacterial genera, which were selected and ranked according to R2 score from single regression analysis (P < 0.05) among 16 genera that were identified through multiple-regression analysis by forward selection (Supplementary Table 3) by using the data of the 217 participants (Supplementary Table 1). B T2DM-related bacterial genera, which are selected and ranked according to R2 score from single regression analysis (P < 0.05) among 22 genera that were identified through multiple logistic regression analysis by forward selection (Supplementary Table 4) by using the data of 192 participants (comprising 147 nonDM subjects and 45 T2DM patients and excluding 25 patients with Type 1 diabetes) (Supplementary Table 1). C Intestinal genera associated with both BMI and T2DM. D Odds ratios for Blautia abundance in the development of obesity (BMI ≥ 25) and T2DM. E Estimation of Blautia species according to BlastN analysis of representative OTU sequences.