Figure 2. T cell exhaustion differentiation includes a point of no return after which impedes immunotherapy efforts.
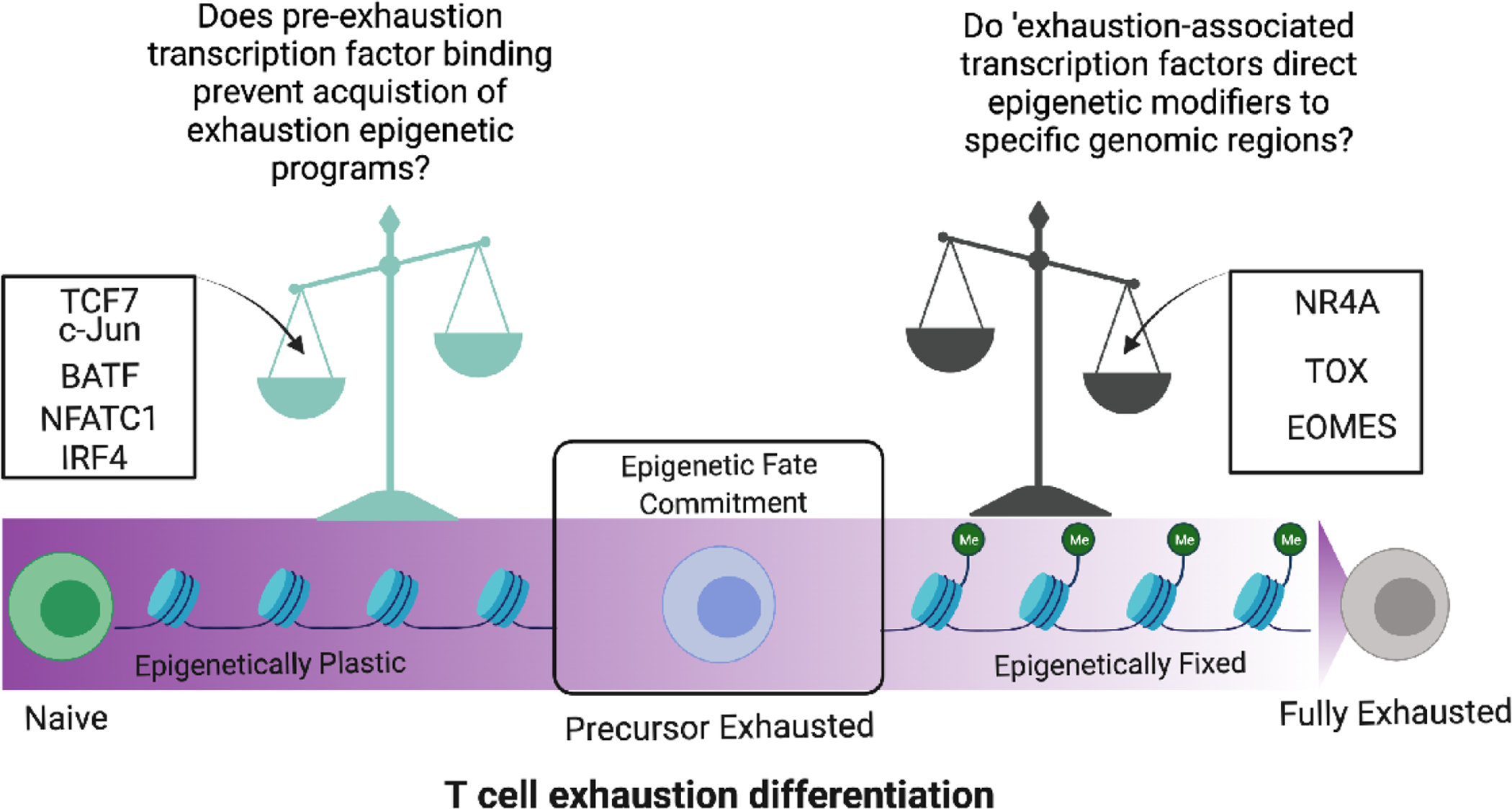
The spectrum of T cell exhaustion differentiation is influenced by the action of several key transcription factors that can either maintain T cells in an epigenetically plastic stem-like state or tip the balance toward terminal exhaustion. An epigenetic checkpoint determines the fate commitment of precursor exhausted T cells which can either become rejuvenated to maintain anti-tumor function or epigenetically fixed in a fully exhausted state.
