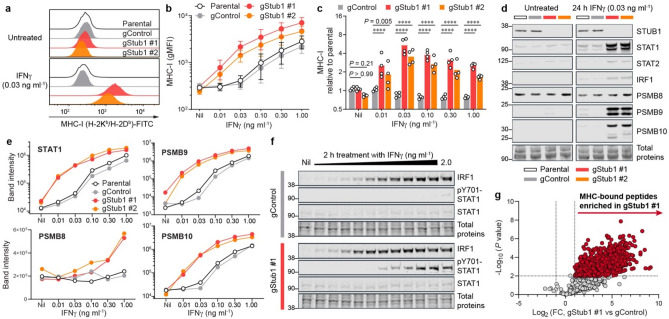
Figure 1.
Stub1 deletion enhances antigen processing and presentation by sensitizing tumour cells to IFNγ. (a–c) Flow cytometry analysis of cell surface MHC-I on parental, control or independent Stub1-null B16-F10 cells. gMFI, geometric mean fluorescence intensity. (d, e) Western blot analysis of the expression level of STUB1, STAT1, STAT2, IRF1, PSMB8, PSMB9 and PSMB10 in parental, control or independent Stub1-null B16-F10 cells. Band intensity was normalized with total protein signal. The tumour cells were either untreated (Nil) or treated with IFNγ for 24 h (a–e). See Supplementary Fig. 1 for additional flow cytometry plots, Western blot data and analysis (a, d, e). (f) Western blot analysis of the expression level of IRF1, STAT1, and phosphorylation of Tyr701-STAT1 at 2 h post-treatment with IFNγ (twofold serial dilution from 2.0 ng ml−1). (g) Volcano plot showing differential presentation of MHC-associated peptide in gStub1 #1 versus gControl cells, following stimulation with 0.03 ng ml−1 IFNγ for 24 h. Red circles highlight peptides significantly enriched in gStub1 #1 cells (twofold cutoff, P ≤ 0.01; n = 3 biological replicates). FC, fold change. See Supplementary Fig. 2d for data of gStub1 #2 cells. Representative of four (a) or two (d–f) independent experiments. Data are mean ± s.d. (b) or mean with all data points (c) from four independent experiments. P values were determined by ordinary two-way ANOVA on Log2-transformed data with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, ****P ≤ 0.0001 (c).