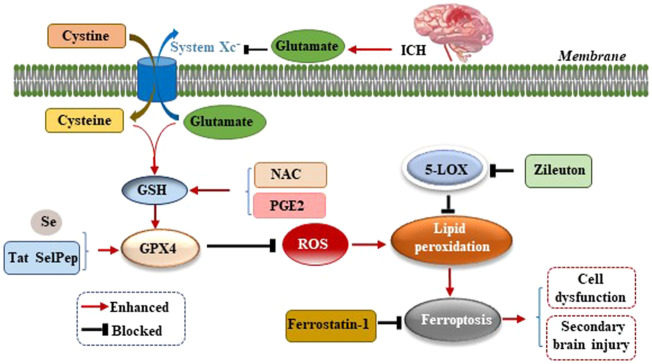
FIGURE 2.
Mechanism of ferroptosis following ICH by inhibiting cystine/glutamate antiporter (System Xc−). After ICH occurs, excessive glutamate (Glu) around neurons inhibits the activity of System Xc− and the transfer of cysteine (Cys), leading to reduction of glutathione (GSH) synthesis, which reduces the activity of glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4), resulting in excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxide levels which cannot be scavenged, thereby leading to neuronal ferroptosis, cell dysfunction, and secondary brain injury (SBI) caused by ICH.