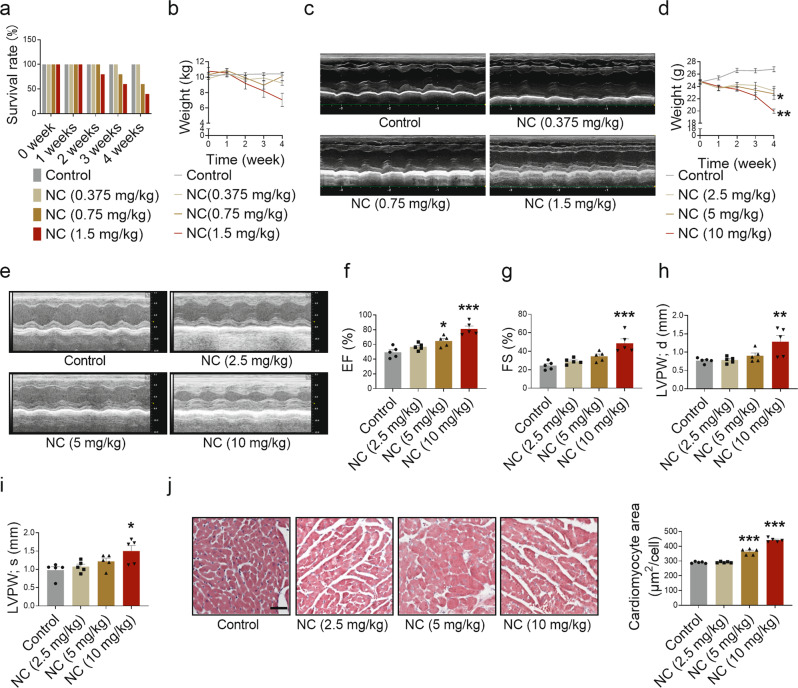
Fig. 3. Cardiotoxicity of NC in beagles and mice.
Beagles were intraperitoneally injected with different doses of NC once a day for 4 weeks and anesthetized for echocardiography. a Beagle death rate during the 4 weeks of NC administration. b Body weight changes of beagles were recorded. c Representative images of the left heart ventricle chamber M-model were collected by echocardiography in beagles. n = 5 beagles in each group at week 0; n = 5 beagles in Control and NC (0.375 mg/kg) groups, n = 3 beagles in NC (0.75 mg/kg) group, and n = 2 beagles in NC (0.375 mg/kg) group in the fourth week. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with different doses of NC once a day for 4 weeks as well. d Body weight changes of mice were recorded. e Diastolic and systolic ultrasonic cardiogram of heart in mice. f–i The quantitative analysis of heart function changes in EF, FS, diastolic LVPW thickness, and systolic LVPW thickness in mice. j The sections of myocardial tissue in mice were stained with H&E (×200) after 4 weeks of NC administration, and the average area of a single cardiomyocyte was statistically analyzed. The red area represents the cytoplasm of cardiomyocytes while the blue area represents the nuclei of cardiomyocytes. Scale bar: 50 μm. n = 5 mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs Control.