Figure 1.
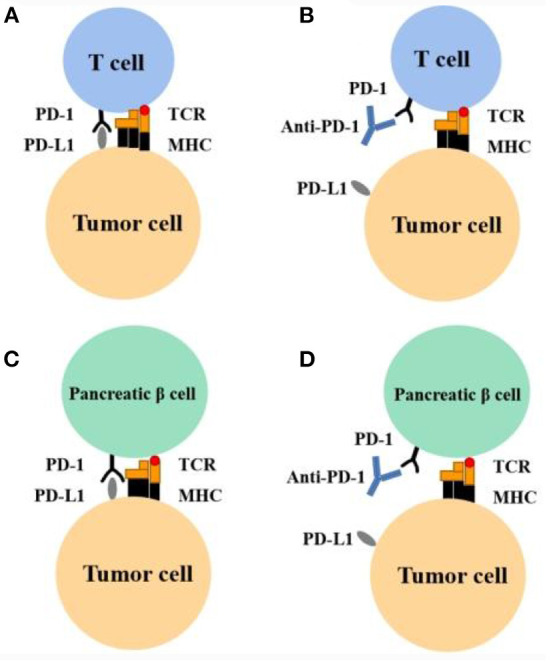
Mechanism of action of PD-1 inhibitor and hypothesis of association between PD-1 inhibitors and type 1 diabetes. (A) Tumor cells can inactivate T cells and evade the immune system by expressing PD-L1. This leads to the enhanced survival of tumor cells. (B) Anti–PD-1 can block the PD-1 receptor and restore immune response. This leads to the apoptosis of tumor cells. (C) Pancreatic β-cells express PD-L1 and thereby evade the immune response. (D) During anti–PD-1 therapy, in certain susceptible persons, T cells are activated and develop an immune response to pancreatic β-cells. MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TCR, T-cell receptor.
