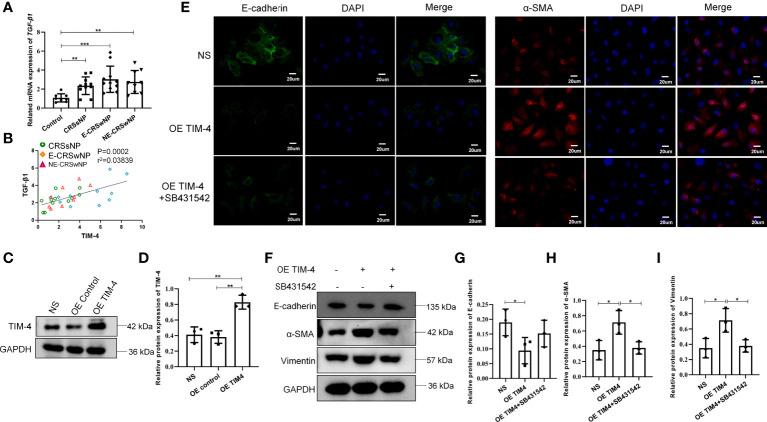
Figure 5.
TIM-4 expression in macrophages contributes to EMT of nasal epithelial cells. (A) The mRNA expression levels of TGF-β1 in different human sinonasal mucosa, as detected by quantitative RT–PCR. (B) The correlation between TIM-4 and TGF-β1. (C) TIM-4 overexpression in THP-1 cells was measured by Western blot analysis. GAPDH was used as a control. (D) Quantitative summary of the relative protein expression of TIM-4. (E) hNECs were cultured with OE TIM-4 THP-1 cells transfected with lentivirus and treated with 10 μmol/L TGF-β1 inhibitor (SB431542) for 24 h. The expression of EMT markers E-cadherin and α-SMA was detected by immunofluorescence. (F) The OE TIM-4 THP-1 cells and RPMI2650 were cocultured and treated with 10 μmol/L TGF-β1 inhibitor (SB431542) for 24 h, and the expression of EMT markers E-cadherin, α-SMA, and Vimentin were detected by Western blot analysis. The intensity values of the bands were normalized to GAPDH expression. (G) Quantitative summary of the relative protein expression of E-cadherin. (H) Quantitative summary of the relative protein expression of α-SMA. (I) Quantitative summary of the relative protein expression of Vimentin. Bars show the mean ± SD. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Representative immunofluorescence images are shown at 400× magnification.