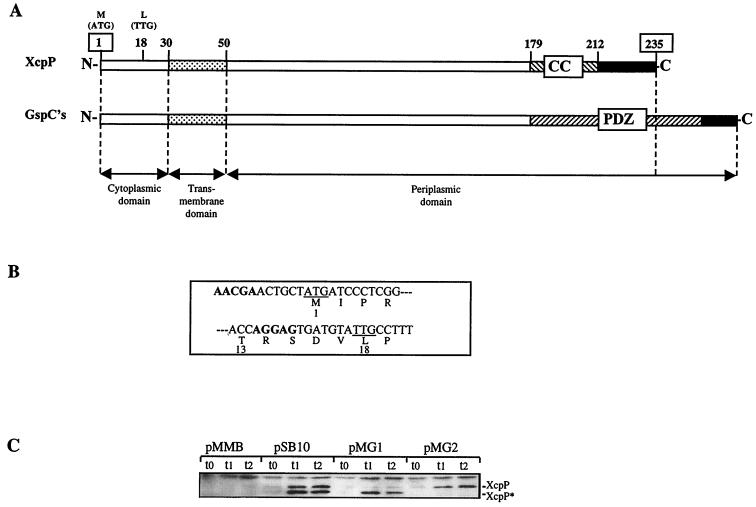
FIG. 1.
(A) Comparison of characteristic features of P. aeruginosa XcpP (235 amino acids) and other GspC members. Shown are the transmembrane domain ( ), coiled-coil region (CC) (▧), PDZ domain (▨), and extreme C terminus (■). The numbers indicated between XcpP domains correspond to residue positions in P. aeruginosa XcpP. The regions corresponding to the cytoplasmic, transmembrane, and periplasmic domains are delimited with double-headed arrows. The position of the alternative N-terminal residue is indicated (L18), and positions of the first and last XcpP residues are boxed. (B) 3′ region of the xcpP gene. The codons for Met1 and Leu18 are underlined. Boldface letters denote DNA stretches corresponding to the putative Shine-Dalgarno sequences. (C) Characterization of two xcpP gene products by immunodetection after separation by electrophoresis in an 11% acrylamide gel. Samples of TG1 producing both XcpP and XcpP* (pSB10), XcpP* only (pMG1), or XcpP only (pMG2) or containing the vector pMMB67HE were taken at various times after addition of IPTG (t0). t1 = 30 min; t2 = 1 h.
), coiled-coil region (CC) (▧), PDZ domain (▨), and extreme C terminus (■). The numbers indicated between XcpP domains correspond to residue positions in P. aeruginosa XcpP. The regions corresponding to the cytoplasmic, transmembrane, and periplasmic domains are delimited with double-headed arrows. The position of the alternative N-terminal residue is indicated (L18), and positions of the first and last XcpP residues are boxed. (B) 3′ region of the xcpP gene. The codons for Met1 and Leu18 are underlined. Boldface letters denote DNA stretches corresponding to the putative Shine-Dalgarno sequences. (C) Characterization of two xcpP gene products by immunodetection after separation by electrophoresis in an 11% acrylamide gel. Samples of TG1 producing both XcpP and XcpP* (pSB10), XcpP* only (pMG1), or XcpP only (pMG2) or containing the vector pMMB67HE were taken at various times after addition of IPTG (t0). t1 = 30 min; t2 = 1 h.