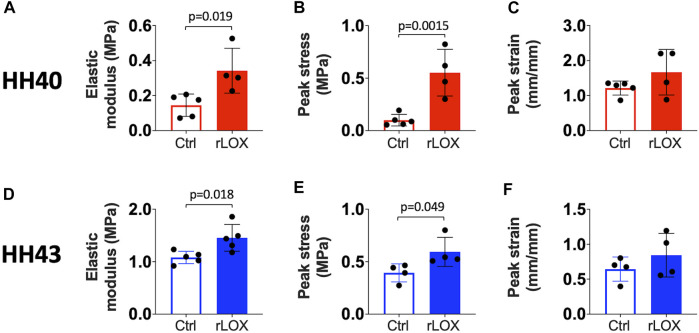
FIGURE 1.
Tensile mechanical properties of HH40 and HH43 tendons were significantly enhanced by rLOX treatment of the tendon during development in vivo. Elastic modulus (A) and peak stress (B) of HH40 tendons increased significantly with rLOX as compared to Ctrl treatment. Peak strain (C) of HH40 tendons was unchanged with rLOX treatment. Elastic modulus (D) and peak stress (E) of HH43 tendons increased significantly with rLOX treatment. Peak strain (F) of HH43 tendons was unchanged with rLOX treatment. Statistically significant differences were determined by Student t-test with p < 0.05. n = 5 per stage and treatment group.