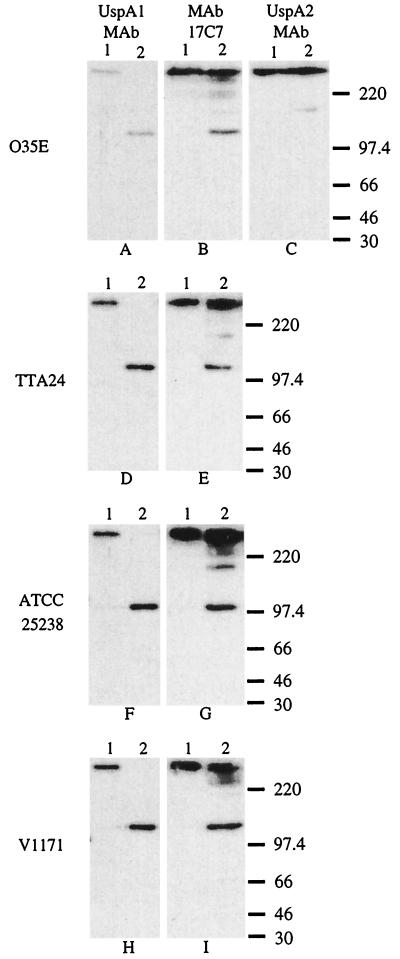
FIG. 2.
Western blot-based detection of UspA1 and UspA2 proteins in selected M. catarrhalis strains. Whole-cell lysates of M. catarrhalis O35E (A, B, and C), TTA24 (D and E), ATCC 25238 (F and G), and V1171 (H and I) were heated in SDS sample buffer at 37°C (lane 1) or at 100°C (lane 2) for 10 min. Panels A, D, F, and H were probed with the UspA1-specific MAb 24B5. As seen in lane 1, this MAb bound the high-molecular-mass form of UspA1 in the 37°C sample. As seen in lane 2, this same MAb bound the putative monomeric 120 to 130 kDa form of UspA1 in the 100°C sample. Panels B, E, G, and I were probed with the UspA1- and UspA2-reactive MAb 17C7. Panel C was probed with the UspA2-specific MAb 17H4 which reacted with the high-molecular-weight aggregate of UspA2 from strain O35E in both the 37°C sample (lane 1) and the 100°C sample (lane 2); heating at this latter temperature did not reduce the size of the UspA2 antigen in this assay system. MAb 17C7 also recognizes aggregates or degradation products from UspA2 as confirmed by previous analysis of isogenic uspA1 and uspA2 mutants of strain O35E (1, 2). Molecular mass position markers (in kDa) are shown on the right side of the figure.