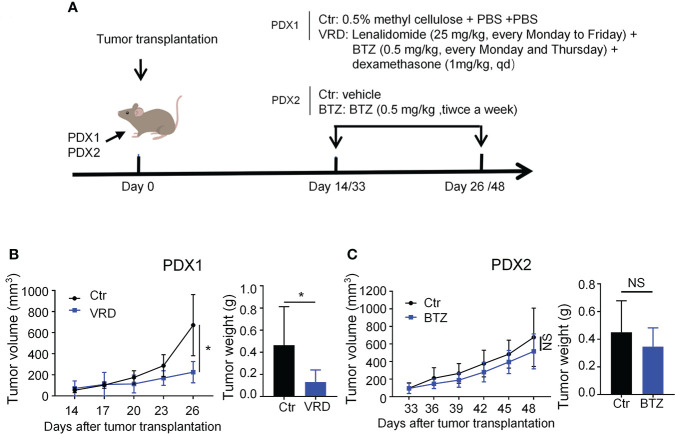
Figure 3.
Newly established myeloma PDXs retained their original drug sensitivity and resistance as seen in the clinic. (A) Experimental design: NDG mice were subcutaneously implanted with tumor pieces (1-2 mm3) of PDXs on the flank. When tumors reached 4-6 mm in diameter, mice were randomly divided into two groups. PDX1 models were treated with the VRD regimen or vehicle control. VRD regimen therapy: tumor-bearing mice (n=4-5 every group) received bortezomib (0.5 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every Monday and Thursday, lenalidomide (25 mg/kg) by intragastric administration every Monday to Friday, and dexamethasone (1 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every day for twelve days, and control group was intragastrically administrated with 0.5% methyl cellulose and phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) intraperitoneally. PDX2 models were treated with bortezomib or vehicle control. Bortezomib therapy: tumor-bearing mice (n=3-4 every group) received bortezomib (0.5 mg/kg) intraperitoneally every Monday and Thursday for a total of 5 doses, and the control group was treated with PBS. (B, C) Tumor size was measured every 3 days, and tumor weight was measured at the end of the treatment. Ctr, the control group; VRD, VRD treatment group; BTZ, bortezomib treatment group; PDX, patient-derived xenograft; NS, no statistically significance. Data were from one experiment representative of two independent experiments with similar results. Data were shown as mean ± SD. Significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. NS, no significance, *P < 0.05.