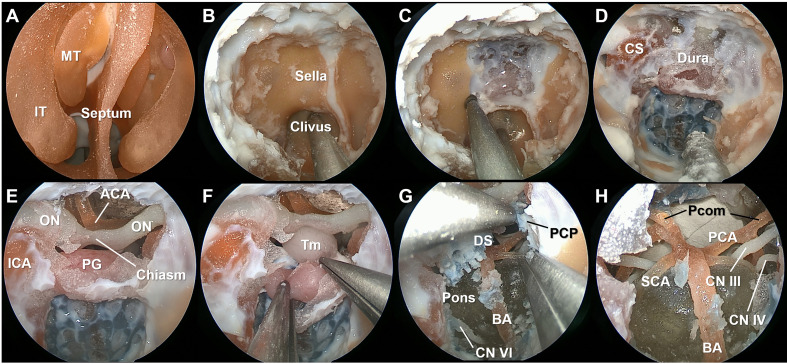
Figure 2.
Stepwise dissection of the endoscopic endonasal surgery procedures using the simulation model. The mucosa and bony structures of the intranasal cavity were identified (A). After wide sphenoidotomy (B), the anterior skull base was drilled to expose the sella, clivus, and anterior wall of the cavernous sinus (C, D). The dura ventral to the brain stem was colored in blue to indicate the basilar venous plexus. Intradural neurovascular structures were observed after opening the dura (E), and the tumor lesion reconstructed from the patient with a stalk originated craniopharyngioma was identified (F). After resection of the dorsum sella and posterior clinoid process, neurovascular structures within the posterior fossa were identified (G, H). IT, inferior turbinate; MT, middle turbinate; ON, optic nerve; ICA, internal carotid artery; ACA, anterior cerebral artery; PG, pituitary gland; BA, basilar artery; Pcom, posterior communicating artery; PCA, posterior cerebral artery; SCA, superior cerebellar artery; CN, cranial nerve.