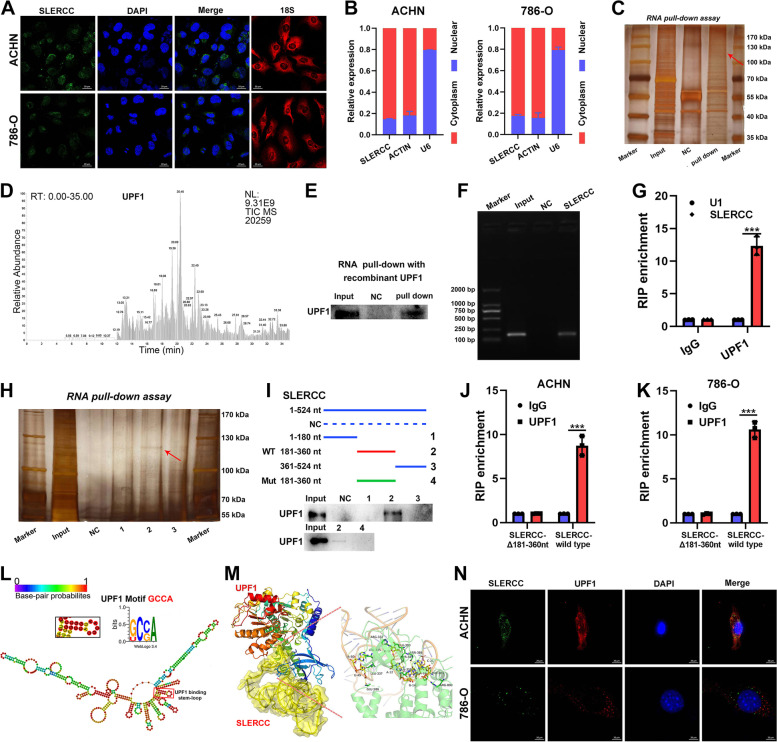
Fig. 6.
SLERCC directly binds to UPF1. A FISH assay to assess the intracellular localization of SLERCC in ACHN and 786-O cells. B qRT-PCR analysis of SLERCC in nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions of ACHN and 786-O cells. C RNA pull-down assay for SLERCC in ACHN cells. D Mass spectrometric (MS) analysis of the proteins from the RNA pull-down assay. E Western blotting after RNA pull-down with recombinant UPF1. F Agarose gel electrophoresis for the RNA pull-down assay shows that UPF1 is a direct target of SLERCC. G RIP assay using anti-UPF1 to assess the enrichment of SLERCC by UPF1. IgG is the negative control, while U1 is a nonspecific control. H, I Serial deletion RNA pull-down assay for SLERCC in ACHN cells. J, K RIP assay after deletion of 181–360 nt from SLERCC in ACHN and 786-O cells. L Prediction of the stem-loop structures at UPF1-binding sites in SLERCC. M PyMOL software displaying the interaction between SLERCC and UPF1 in their 3D protein structures. N FISH to assess the colocalization of SLERCC and UPF1 in ACHN and 786-O cells. (***p < 0.001). Abbreviations: TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas; FISH, Fluorescence in situ hybridization; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation