Extended Data Fig. 3. Reduction in cardiometabolic risk associated with lower frequency of depressed mood among individuals at high polygenic risk.
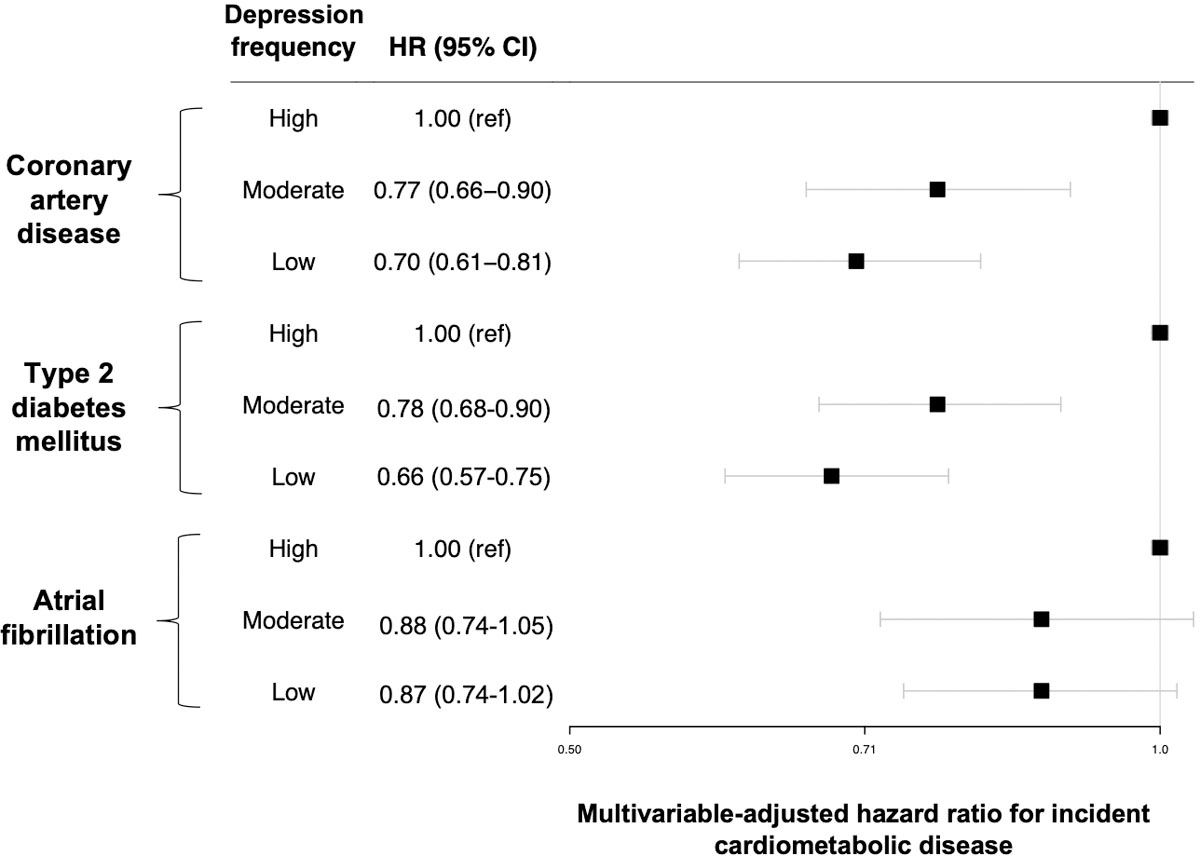
Data are presented as hazard ratios (black squares) and 95% confidence intervals (error bars). Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios are calculated among 60,849 individuals without prevalent coronary artery disease (2,510 with high, 11,305 with moderate, and 47,034 with low frequency of depressed mood); 62,974 individuals without prevalent type 2 diabetes (2,520 with high, 11,622 with moderate, and 48,832 with low frequency of depressed mood); and 63,414 individuals without prevalent atrial fibrillation (2,573 with high, 11,683 with moderate, and 49,158 with low frequency of depressed mood). Hazard ratios (left) are adjusted for age, age2, sex, the first 20 principal components of ancestry, genotyping array, country, socioeconomic deprivation, smoking status, pack-year smoking history, alcohol intake, vegetable and fresh fruit intake, days per week of moderate and vigorous exercise, sleep duration, systolic blood pressure, antihypertensive medication use, non-HDL cholesterol, cholesterol-lowering medication use, antiplatelet medication use, antihyperglycemic medication use, prevalent type 2 diabetes mellitus (models for coronary artery disease and atrial fibrillation only), body-mass index, and C-reactive protein.
