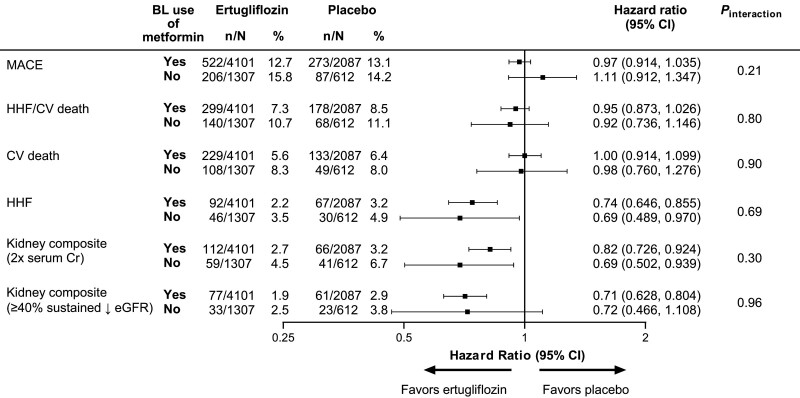
Figure.
Cardiovascular and kidney outcomes with ertugliflozin versus placebo by baseline metformin use after propensity adjustment for metformin use. Differences in risk of cardiovascular and kidney outcomes between ertugliflozin and placebo across subgroups by baseline metformin use were estimated from a Cox proportional hazards model by means of propensity adjustment for metformin use by using inverse probability of treatment weighting to account for differences in baseline characteristics and risk factor profiles between patients with and without baseline metformin use. Treatment, baseline metformin use, and the interaction term between treatment and baseline metformin use were included in each model, and the enrollment cohort was included as a stratification factor. Model weights were calculated using propensity score estimates of baseline metformin use and the inverse probability of treatment weighting formula. The variables considered in propensity scoring were age, sex, race, region, body mass index, duration of type 2 diabetes, glycated hemoglobin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and history of: coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, peripheral arterial disease, heart failure, myocardial infarction, coronary artery bypass graft, percutaneous coronary intervention, and stroke. Hazard ratios (95% CIs) are provided for ertugliflozin versus placebo by baseline metformin use. The interaction P value is shown for the 2-level treatment group (all ertugliflozin versus placebo). The kidney composite outcomes were doubling of serum creatinine level, kidney replacement therapy, or death from kidney causes and the exploratory kidney outcome of sustained ≥40% decrease in eGFR from baseline, kidney replacement therapy, or death from kidney causes. BL indicates baseline; Cr, creatinine; CV, cardiovascular; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HHF, hospitalization for heart failure; and MACE, major adverse cardiovascular events.