FIGURE 2.
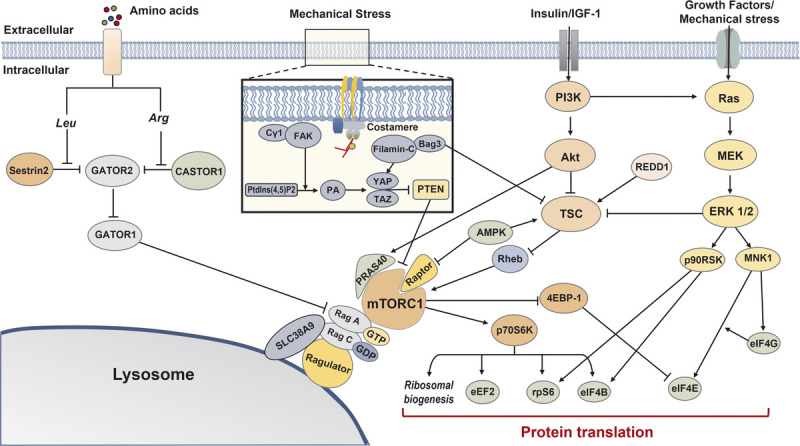
Overview of mTORC1-related protein synthesis pathways. Multiple signaling cascades converge on mTORC1 and contribute to protein translation. Cytosolic leucine and arginine relieve inhibition on GATOR2 by Sestrin2 and CASTOR1, respectively, and subsequently promote mTORC1-induced protein synthesis via GATOR2–GATOR1–Rag signaling. Mechanical stress causes Cγ1 to colocalize around FAK, catalyzing Ptdlns(4,5)P2 conversion to PA, and subsequently activates the HIPPO pathway (YAP and TAZ). Filamin-C and Bag3 interaction also activates the HIPPO pathway. The HIPPO pathway promotes mTORC1 signaling via the suppression of PTEN. The PI3K–Akt–TSC signaling cascade regulates mTORC1 signaling via Rheb, although Akt can directly promote mTORC1 signaling via PRAS40. AMPK and REDD1 inhibit mTORC1 via TSC; AMPK can also inhibit mTORC1 directly via Raptor. mTORC1 promotes protein synthesis by activating several translational and ribosomal components, and Ras–MEK–ERK 1/2 signaling converges on common factors. 4EBP-1, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1; Akt, protein kinase B; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; Arg, arginine; eEF2, eukaryotic elongation factor 2; eIF4B, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4B; eIF4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E; eIF4G, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4G; ERK 1/2, extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2; FAK, focal adhesion kinase; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor 1; Leu, leucine; MEK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; MNK1, MAP kinase-interacting kinase 1; mTORC1, mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1; p70S6K, p70 S6 kinase 1; p90RSK, p90 ribosomal protein S6 kinase; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PRAS40, proline-rich AKT substrate 40 kDa; PtdIns(4,5)P2, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate; PTEN, phosphatase and tensin homolog; Raptor, regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; REDD1, regulated in development and DNA damage responses 1; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain; rpS6, ribosomal Protein S6; TAZ, transcriptional coactivator with PDZ-binding motif; TSC, tuberous sclerosis complex; YAP, Yes-associated protein 1.
