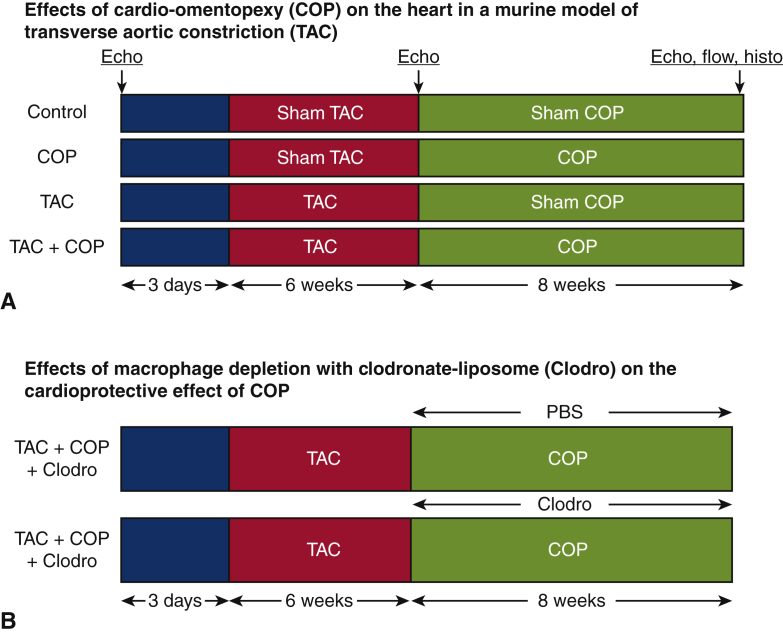
Figure 1.
Experimental protocol. A, Effects of cardio-omentopexy (COP) on the heart in a murine model of transverse aortic constriction (TAC). In the TAC+COP group, C57BL/6 mice were subjected to TAC for 6 weeks and subsequently COP for 8 weeks. The transverse aorta was constricted between the innominate and left common carotid arteries using a 7-0 prolene suture ligature tied against a 25-gauge blunted needle. The pedicled greater omentum with the right gastroepiploic artery was transferred to the heart through the diaphragm. Mice in TAC and COP groups underwent TAC or COP alone. Control mice underwent all surgical procedures without the TAC and/or connection of the greater omentum with the heart. B, Effects of macrophage depletion with clodronate-liposome (Clodro) on the cardioprotective effect of COP. The geometry and function of the left ventricle was evaluated with echocardiography (Echo). Flow cytometry (flow) was conducted to analyze macrophage subsets in mouse hearts, and mouse hearts received histopathological examination (histo) to determine cardiomyocyte size, fibrosis, and microvessel density.