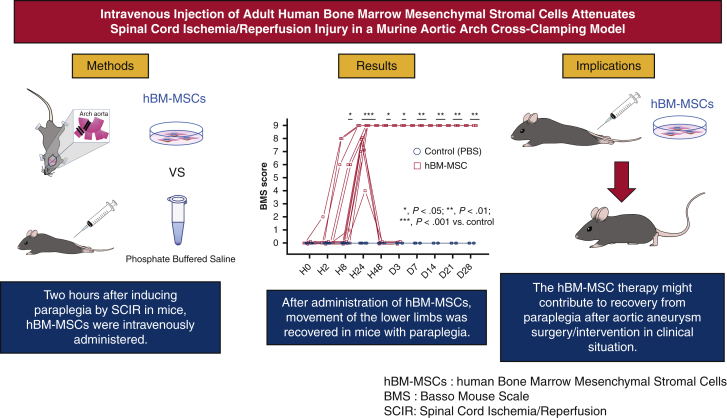
Figure 8.
We sought to investigate the efficacy of hBM-MSCs in a murine SCIR model. C57BL/6J mice were subjected to SCIR by crossclamping the aortic arch and left subclavian artery for 5.5 minutes. Two hours after reperfusion, hBM-MSCs (hBM-MSC group) or phosphate-buffered saline (control group) were intravenously injected without immunosuppressant. Hindlimb motor function was assessed until day 28 after reperfusion using the BMS. BMS score was 0 throughout the study period in all control mice. BMS score was significantly greater in the hBM-MSC group than the control group from hour 8 (P < .05) to day 28 (P < .01). The numbers of motor neurons at hour 24 (P < .01) and day 28 (P < .05) were significantly preserved in the hBM-MSC group than the control group. The hBM-MSC therapy might contribute to recovery from paraplegia after aortic aneurysm surgery/intervention in clinical situation. hBM-MSC, Human bone marrow mesenchymal stem/stromal cell; SCIR, spinal cord ischemia/reperfusion BMS, Basso Mouse Scale.