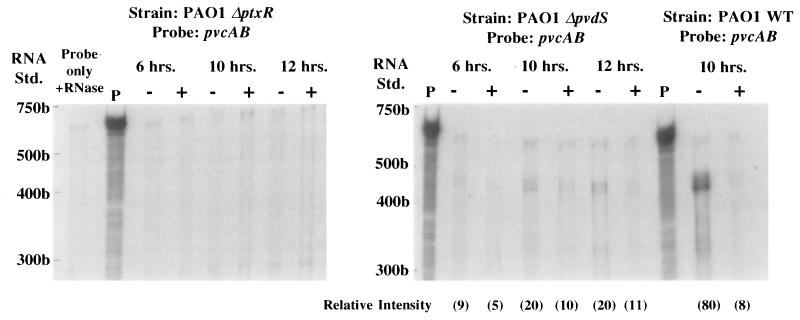
FIG. 3.
RNase protection analysis of pvcABCD gene expression in the PAO1 parental strain (PAO1 WT) and PAO1 strains which carry deletion mutations in the ptxR (PAO1 ΔptxR) or pvdS (PAO1 ΔpvdS) genes. RNA samples were extracted from cells grown continuously for 6, 10, or 12 h in medium that was either iron deficient (−) or iron replete (+), and protection against RNase digestion was afforded by the pvcAB probe assessed as described in Materials and Methods. Undigested (P) and RNase treated (Probe only + RNase) 32P-labelled probes are also shown. The positions of 32P-labelled RNA standards (Std.) are shown to the left of each gel. The gels shown in this figure were exposed for 16 h. The relative intensity of the major band in each lane (in parentheses) was determined by using NIH Image software (version 1.55). As no pvcAB-protected fragment (400 to 500 bp range) was observable in the PAO ΔptxR lanes, relative intensities were not assessed. Riboprobing of total RNA from PAO1 ΔptxR with omlA (not iron regulated) yielded protected fragments with relative intensities of 155 (6 h, iron deficient), 158 (6 h, iron replete), 170 (10 h, iron deficient), 136 (10 h, iron replete), 176 (12 h, iron deficient), and 184 (12 h, iron replete). Riboprobing of total RNA from PAO1 ΔpvdS with omlA yielded protected fragments with relative intensities of 189 (6 h, iron deficient), 192 (6 h, iron replete), 174 (10 h, iron deficient), 143 (10 h, iron replete), 175 (12 h, iron deficient), and 176 (12 h, iron replete).