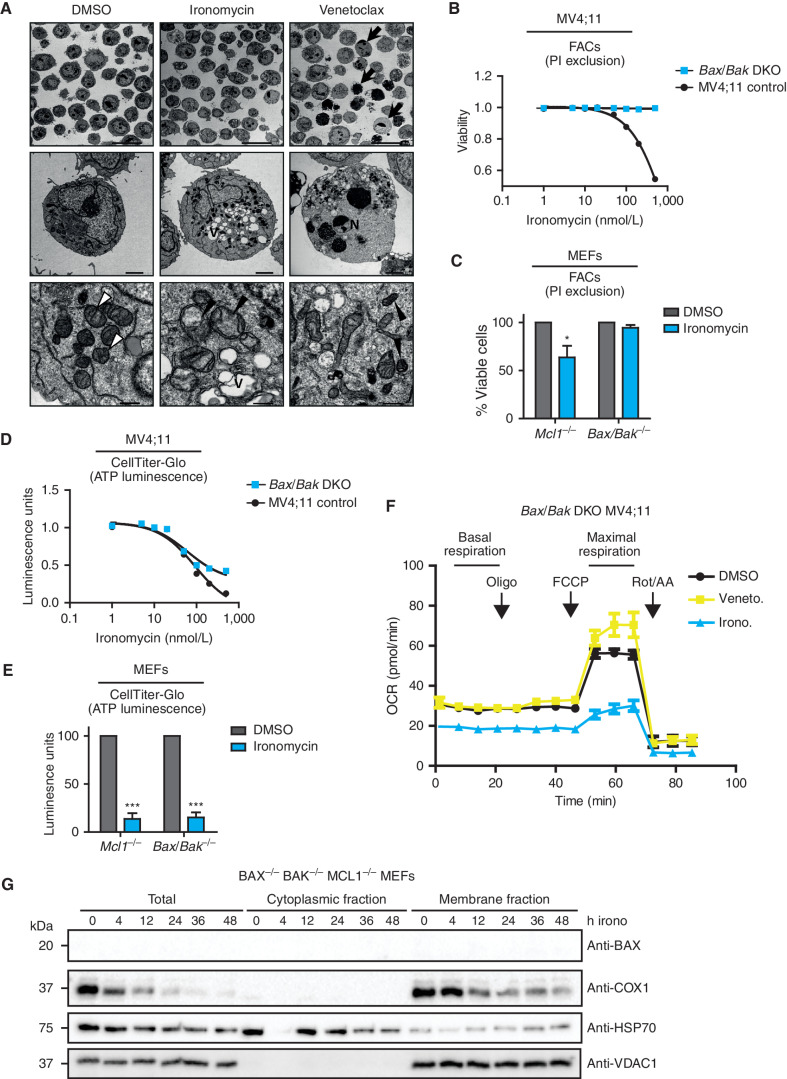
Figure 5.
Ironomycin-induced cell death is BAX/BAK dependent. A,TEM images of MV4;11 cells treated with vehicle (DMSO), 500 nmol/L ironomycin or 50 nmol/L venetoclax for 36 hours. Arrows, examples of apoptotic cells; V, vacuolization; N, chromatin condensation and nuclear fragmentation; white arrowheads, standard mitochondrial morphology; black arrowheads, changed mitochondrial morphology (cristae reduction and dilation, fragmentation, or dark condensed matrix). Scale bars, 20 μm, top; 2 μm, middle; 500 nm, bottom. B, Cell death assessed by PI exclusion using FACS in MV4;11 WT and BAX/BAK DKO cell lines after 48 hours of ironomycin (n = 3 biological replicates). C, Cell death assessed by PI exclusion using FACS in MEF cells treated for 48 hours with 2 μmol/L ironomycin. We compared a Bax−/−Bak−/− with a control Mcl1−/− MEF cell line (n = 3 biological replicates; means ± SEM; *, P < 0.05). D, ATP luminescence measured by CellTiter-Glo in MV4;11 WT and BAX/BAK DKO cell lines after 48 hours of ironomycin (n = 3 biological replicates). E, ATP luminescence measured by CellTiter-Glo in MEF cells treated for 48 hours with 2 μmol/L ironomycin. We compared a Bax−/−Bak−/− with a control Mcl1−/− MEF cell line (n = 3 biological replicates; means ± SEM; ***, P < 0.001). F, Seahorse assay measuring mitochondrial basal and maximal respiration in BAX/BAK DKO MV4;11 cells. We treated the cells for 6 hours with 500 nmol/L ironomycin or 50 nmol/L venetoclax (n = 3 biological replicates). G, Fractionation experiment showing BAX and COX1 protein expressions by immunoblot in total cell, cytosolic fraction, and mitochondrial membrane fraction. The nonheme protein VDAC1 was used as a loading marker of membrane fraction and HSP70 as a loading marker of cytoplasmic fraction. We used the Bax−/−Bak−/−Mcl1−/− MEF cell line and treated cells with 500 nmol/L ironomycin.