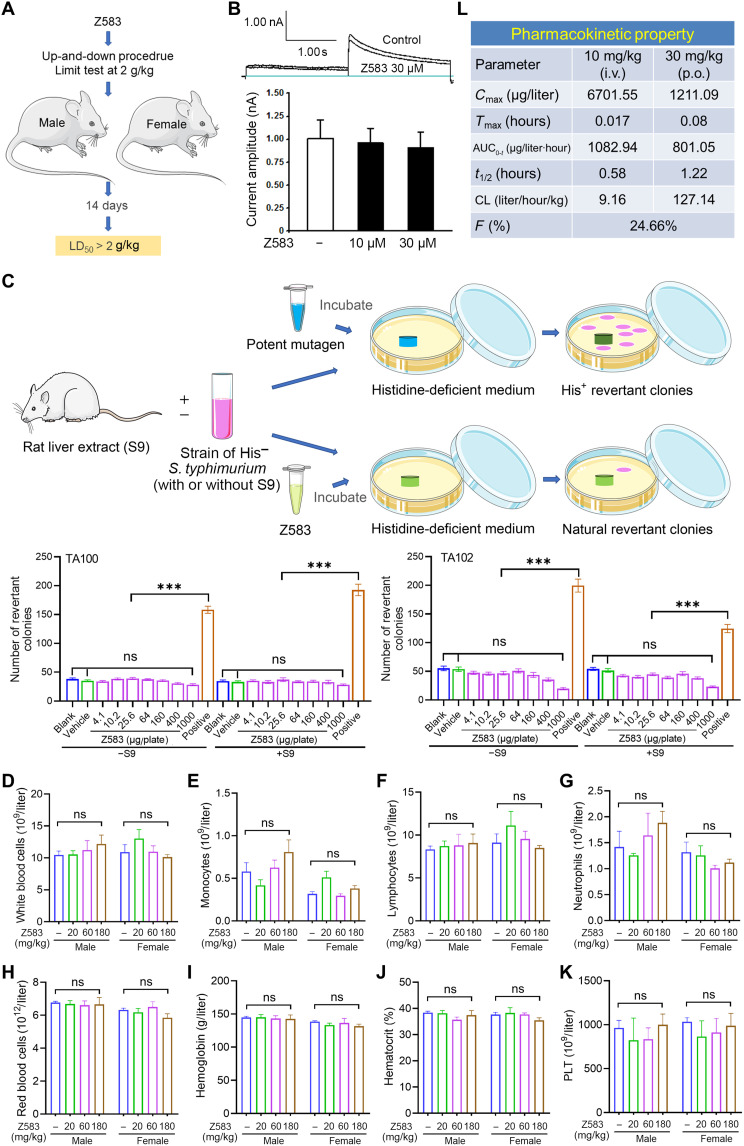
Fig. 7. Safety and pharmacokinetic property of Z583.
(A) Signal dose acute oral toxicity was performed by up-and-down procedure according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development for chemical testing guidelines no. 425 and limited test with single dose at 2 g/kg. (B) Chinese hamster ovary cells were used to measure the possible inhibition of Z583 for hERG potassium current by patch-clamp recording. (C) S. typhimurium strains TA100 and TA102 were used to evaluate the mutagenic potentials of Z583 by bacterial reverse mutation assay; data are presented as means ± SEM, n = 3; ***P < 0.001 versus positive control; ns, no statistical significance of positive group versus blank or vehicle group. White blood cells (D), monocytes (E), lymphocytes (F), neutrophils (G), red blood cells (H), hemoglobin (I), hematocrit (J), and platelets (K) were measured in the blood of rats dosed for 4 weeks with Z583 at 20, 60, and 180 mg/kg (n = 10); data are presented as means ± SEM. ns, no statistical significance of control group versus three treatment group. (L) Preliminary pharmacokinetic property of Z583 by oral (p.o.) and intravenous (i.v.) route in mice (n = 8) was analyzed by LC-MS/MS.