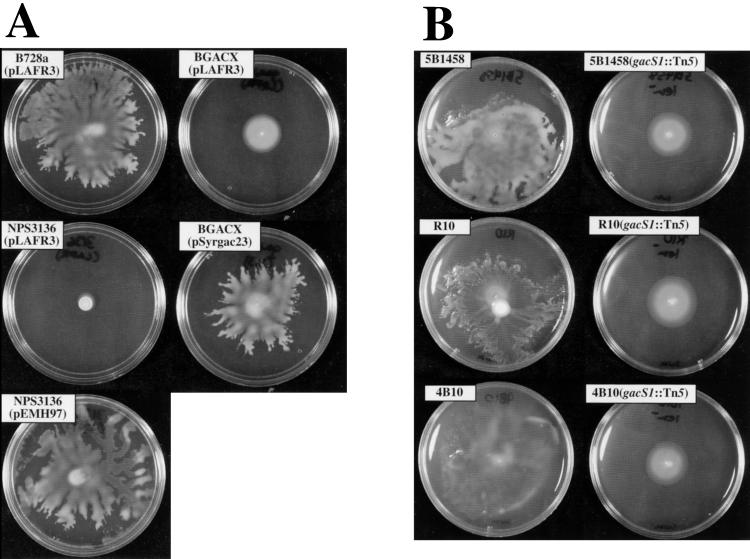
FIG. 1.
(A) Swarming ability of B728a and mutant derivatives. Cells were inoculated with an applicator stick to the center of an SWM plate (5 g of peptone, 3 g of yeast extract, and 4 g of granulated agar per liter; all medium components are from Difco) supplemented with 5 μg of tetracycline per ml to provide plasmid selection. Results were obtained after approximately 48 h of incubation at 28°C. NPS3136 (25) and BGACX (23) are gacS and gacA insertion mutants, respectively. The ability to swarm is restored to the appropriate mutant by plasmid-borne copies of gacS (i.e., pEMH97) (11) and gacA (i.e., pSyrgac23) (20), but not by the plasmid vector pLAFR3. The surface colony sizes of NPS3136(pLAFR3) and BGACX(pLAFR3) are about the same, with the larger apparent diameter of BGACX(pLAFR3) resulting from growth inside the agar matrix (see text). SWM medium in all swarming figures in this report was also supplemented with 1% potato infusion broth; this was done for consistency with other work in our laboratory and has no effect on swarming. (B) Swarming ability of field isolates and gacS mutant derivatives (19). Strains were inoculated on SWM medium (described above [B]) without tetracycline. Pictured are results after approximately 48 h of incubation at 28°C. Most of the visible growth of the gacS mutants represents subsurface spreading within the agar matrix, with the lighter spot at the center being the surface colony.