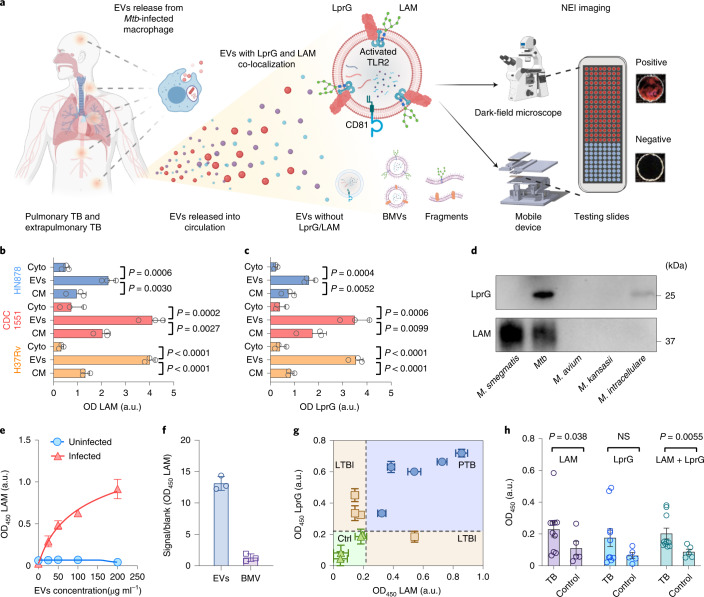
Fig. 1. EV LAM and LprG expression as a biomarker for TB diagnosis.
a, Rationale and assay schematic. Created with BioRender.com. b,c, Western blot densitometry of LAM (b) and LprG (c) expression in cytosolic (Cyto), EV and cell membrane (CM) factions of macrophage cultures infected with the indicated Mtb strains. Data indicate mean ± s.d., n = 3 biologically independent repeats; P values obtained by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-test. a.u., arbitrary units. d, Western blot analysis of LAM and LprG from CFP samples of patients with sequence-confirmed M. smegmatis, Mtb, M. avium, M. intracellulare and M. kansasii infections. e,f, EV-ELISA for LAM on EVs from Mtb-infected macrophages (e) and BMVs isolated from Mtb culture medium (f) by ultracentrifugation when captured by host EV-specific antibody. g, EV-ELISA for LAM and LprG on serum EVs of non-human primates with pulmonary TB (PTB), LTBI or their healthy controls (Ctrl) (mean ± s.d. of three technical replicates). h, EV-ELISA for LAM, LprG and integrated LAM and LprG (LAM+LprG) expression on isolated EVs from serum of children with TB (N = 10) and without evidence of TB (Ctrl; N = 5). Mean ± s.e.m., P values obtained by two-sided Mann-Whitney U test.