Figure 6:
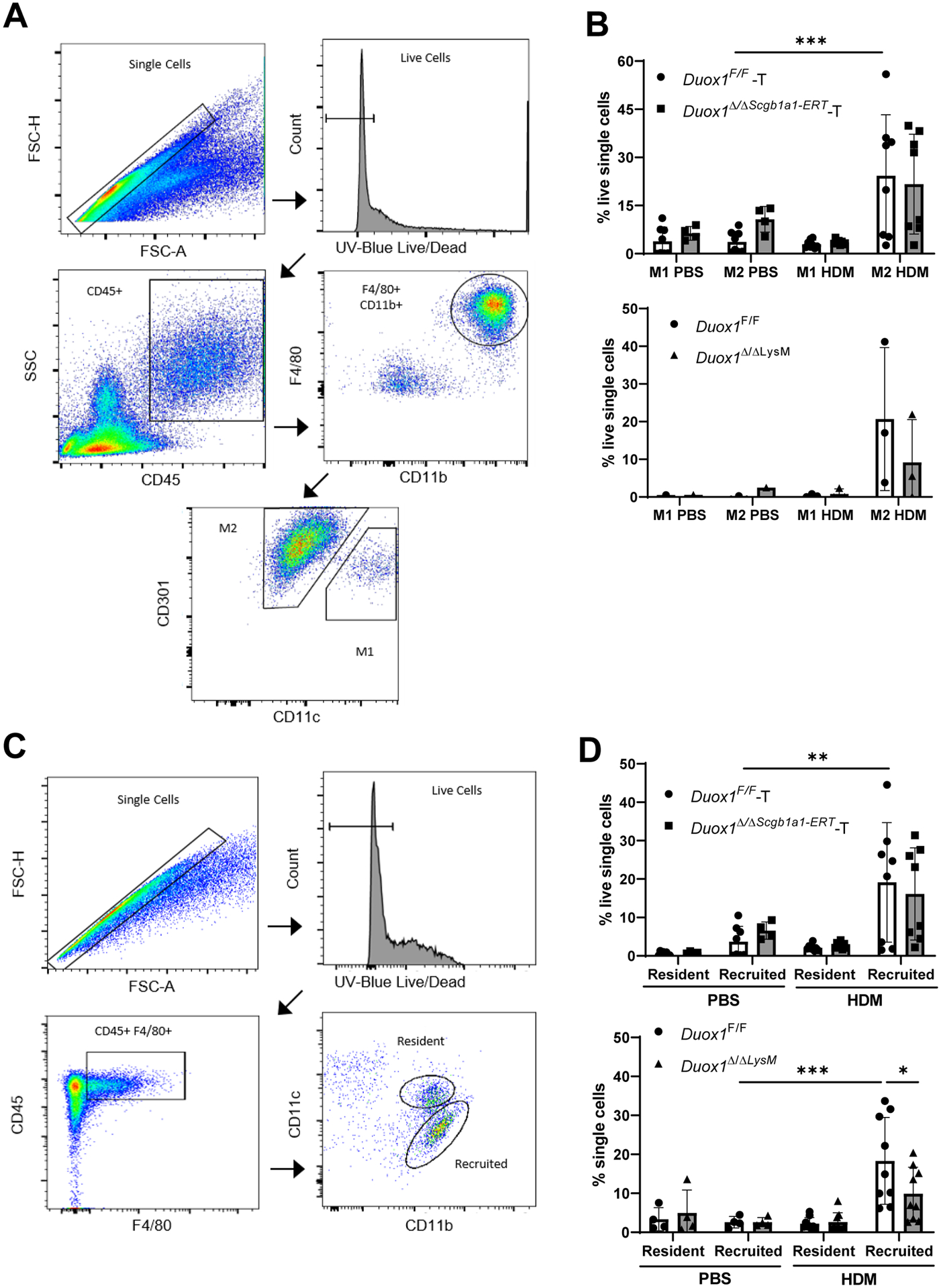
Macrophage-intrinsic DUOX1 contributes to macrophage recruitment during chronic HDM challenge. Mice were subjected to chronic HDM and lung single cell suspensions were evaluated for macrophage polarization. (A) Gating strategy to assess M1/M2 macrophage populations. (B) Quantification of M1 and M2 macrophage populations in lung tissues from tamoxifen-treated Duox1F/F and Duox1Δ/ΔScgb1a1-ERT mice (above) or Duox1F/F and Duox1Δ/ΔLysM mice (below) in response to chronic HDM challenge. Data are presented as a percentage of viable single cells. (C) Gating strategy for flow analysis of resident and recruited macrophage populations. (D) Quantification of resident and recruited macrophage populations in lung tissues from tamoxifen-pretreated Duox1F/F or Duox1Δ/ΔScgb1a1-ERT mice (above), or from Duox1F/F or Duox1Δ/ΔLysM mice (below), after chronic HDM challenge. Data are presented as a percentage of viable, single cells. Statistical significance was evaluated using 2-way ANOVA and Šidák’s post-hoc test. *: p<0.05**: p<0.01; ***: p<0.001 (n = 4–8 mice per group from 2 independent experiments, except bottom panel B which is one representative experiment in triplicate).
