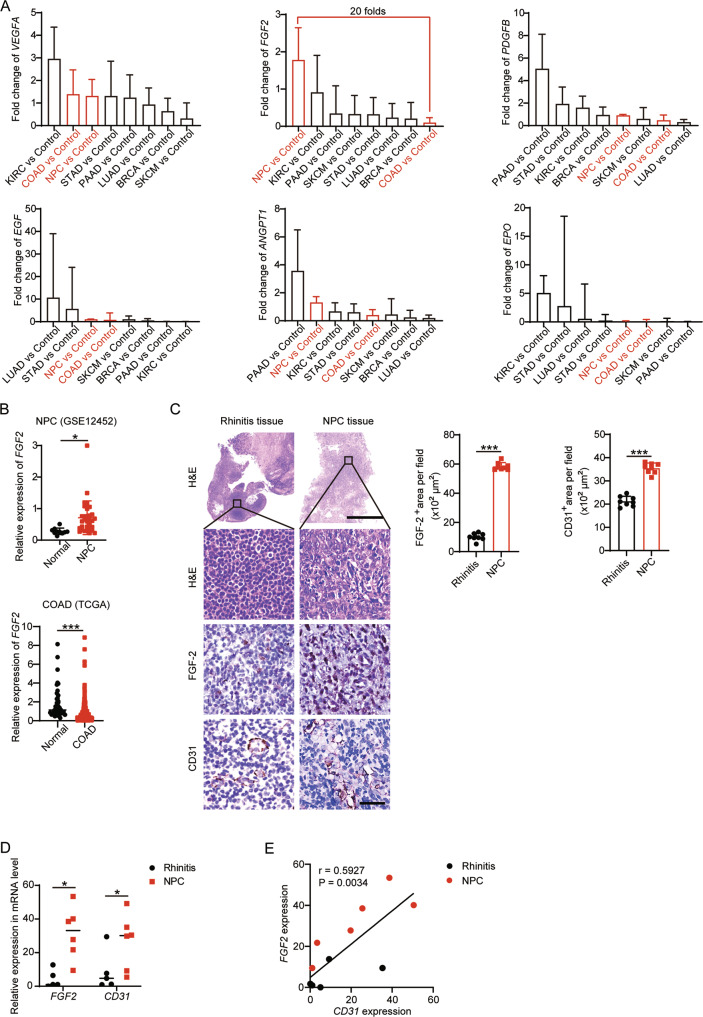
Fig. 2. FGF-2 expression in NPC correlates with tumor vasculature.
A Transcriptomic expression levels of angiogenic factors, including VEGFA, FGF2, PDGFB, EGF, ANGPT1, EPO in human KIRC tissues, COAD tissues, NPC tissues, STAD tissues, PAAD tissues, LUAD tissues, BRCA tissues, SKCM tissues, and their adjacent healthy tissues. The red line indicates the highest expression of FGF2 in AAD-resistant NPC and the lowest expression of FGF in AAD-sensitive CRC. B Transcriptomic expression levels of FGF2 in NPC tissues, COAD tissues, and their adjacent healthy tissues (sample number: control-NPC/NPC/control-COAD/COAD = 10/31/41/290). Data were extracted from datasets GSE12452 and TCGA. C Human rhinitis tissues and NPC tissues were collected and detected for histology (H&E), FGF-2, and CD31 expression levels. Scale bar in upper panel = 500 μm, scale bar in lower three panels = 50 μm. Quantification of FGF-2+ or CD31+ signals (n = 8 random fields per group). D QPCR quantification of FGF2 and CD31 expression in freshly collected rhinitis tissues and NPC tissues (rhinitis tissue, n = 5 samples; NPC tissue, n = 6 samples). E Correlation of FGF2 and CD31 transcriptomic expression levels of human NPCs and control rhinitis tissues (Rhinitis tissue, n = 5 samples; NPC tissue, n = 6 samples). *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001. NS not significant. Data presented as mean ± SD. KIRC kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, COAD colon adenocarcinoma, STAD stomach adenocarcinoma, PAAD pancreatic adenocarcinoma, LUAD lung adenocarcinoma, BRCA breast invasive carcinoma, SKCM skin cutaneous melanoma.