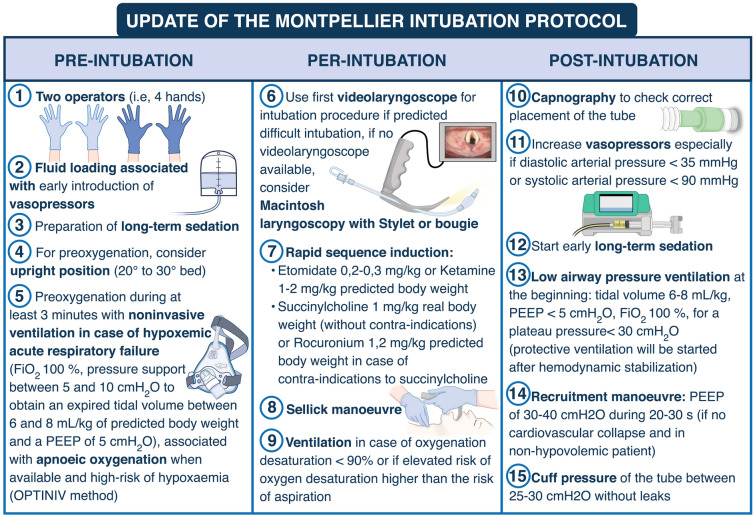
Fig. 3.
Update of the Montpellier intubation protocol. Briefly, pre-intubation period interventions consist in fluid loading associated with early introduction of vasopressors, preoxygenation with NIV in the case of acute respiratory failure, preparation of sedation by the nursing team and the presence of two operators. NIV is applied during the 3-min preoxygenation phase with an ICU ventilator and a standard face mask. The PSV level is set between 5 and 10 cmH2O, adjusted to obtain an expired tidal volume of 6 to 8 ml/kg of ideal body weight. The FiO2 is set at 100% and the PEEP level of 5 cmH2O. During the intubation period, recommended induction is rapid sequence induction using short acting, well-tolerated hypnotics (etomidate or ketamine), and a rapid-onset muscle relaxant (succinylcholine or rocuronium), with application of cricoid pressure (Sellick maneuver). The Sellick maneuver is performed to prevent gastric contents from leaking into the pharynx, by external obstruction of the esophagus, and associated inhalation of substances into the lungs, as well as vomiting into an unprotected airway. Just after the intubation (post-intubation period), we recommend verification of the tube’s position by capnography (a technique which allows to confirm the endotracheal position of the tube and to verify the absence of esophageal placement), initiation of long-term sedation as soon as possible (to avoid agitation) and use of “protective” mechanical ventilation settings, as defined by the ARDS network