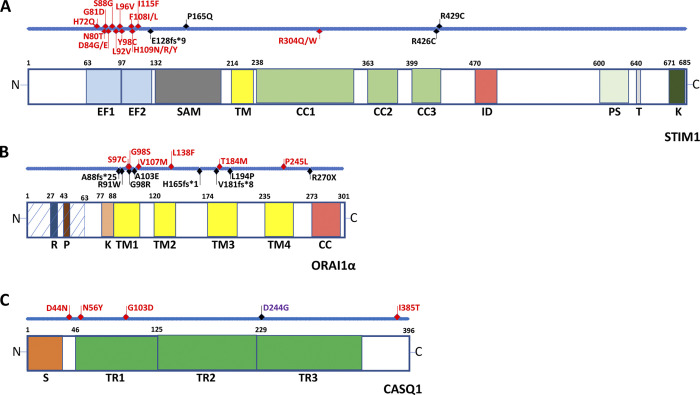
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of STIM1, ORAI1α, and CASQ1 with position of TAM/Stormorken and CRAC channelopathy mutations. (A–C) Schematic representation of STIM1 (A), ORAI1α (B), and CASQ1 (C) with position of TAM/Stormorken and CRAC channelopathy mutations (depicted in red and in black, respectively) aligned with corresponding protein structural regions. D244G CASQ1 mutation (violet) causes vacuolar aggregate myopathy. The position of the initial aa of each protein domain is indicated. Light blue striped box in the N-terminal portion of ORAI1α indicates the region that is not present in the ORAI1β isoform. For STIM1: CC1/2/3, coiled-coil regions 1/2/3; EF1/2, EF-hand motif 1/2; ID, inhibitory domain; K, lysine-rich region; PS, proline/serine-rich region; S, signal peptide; SAM, sterile α-motif; T, TRIP domain; TM, transmembrane domain; for ORAI1α: CC, coiled-coil domain; P, proline-rich region; R, arginine-rich region; RK, arginine/lysine-rich region; TM 1/2/3/4, transmembrane domain 1/2/3/4; and for CASQ1: S, signal peptide; TR1/2/3, thioredoxin domain 1/2/3.