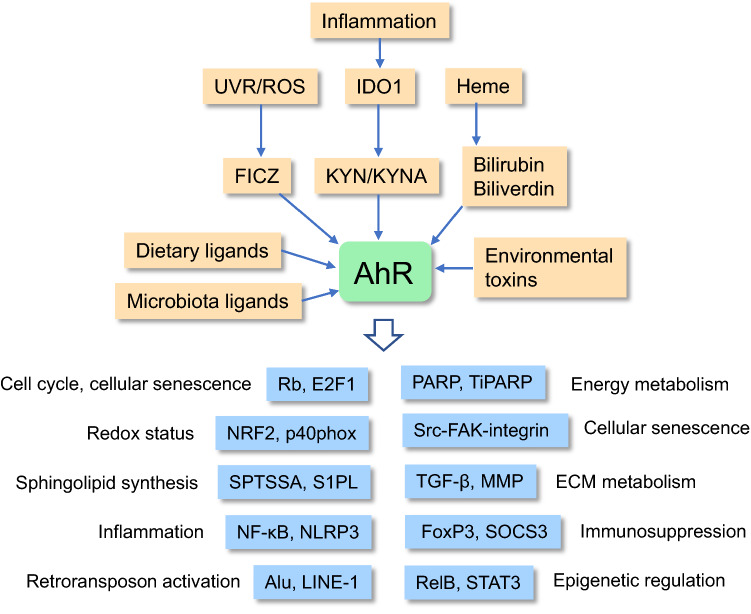
Fig. 2.
Age-related properties induced by the ligand-activated AhR signaling. A large variety of endogenous and exogenous ligands activate AhR signaling which promotes the aging process in a context-dependent manner. Certain dietary, environmental, and microbiota ligands can be antagonists for AhR activation (see text). E2F1 E2F transcription factor 1, FAK focal adhesion kinase, FICZ 6-formylindolo[3,2-b]carbazole, FoxP3 forkhead box P3, IDO1 indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, KYNA kynurenic acid, KYN kynurenine, MMP matrix metalloproteinase, NF-κB nuclear factor-κB, NLRP3 NOD- LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3, NRF2 nuclear factor-erythroid factor 2-related factor 2, p40phox p40 component of NADPH oxidase, PARP poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, Rb retinoblastoma, RelB RELB proto-oncogene, ROS reactive oxygen species, SOCS3 suppressor of cytokine signaling 3, SPTSSA serine palmitoyltransferase small subunit A, Src SRC proto-oncogene, STAT3 signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, TiPARP TCDD-inducible poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, TGF-β transforming growth factor-β, UVR ultraviolet radiation