Figure 1. CD24 deficiency aggravates diet-induced metabolic disorder in mice.
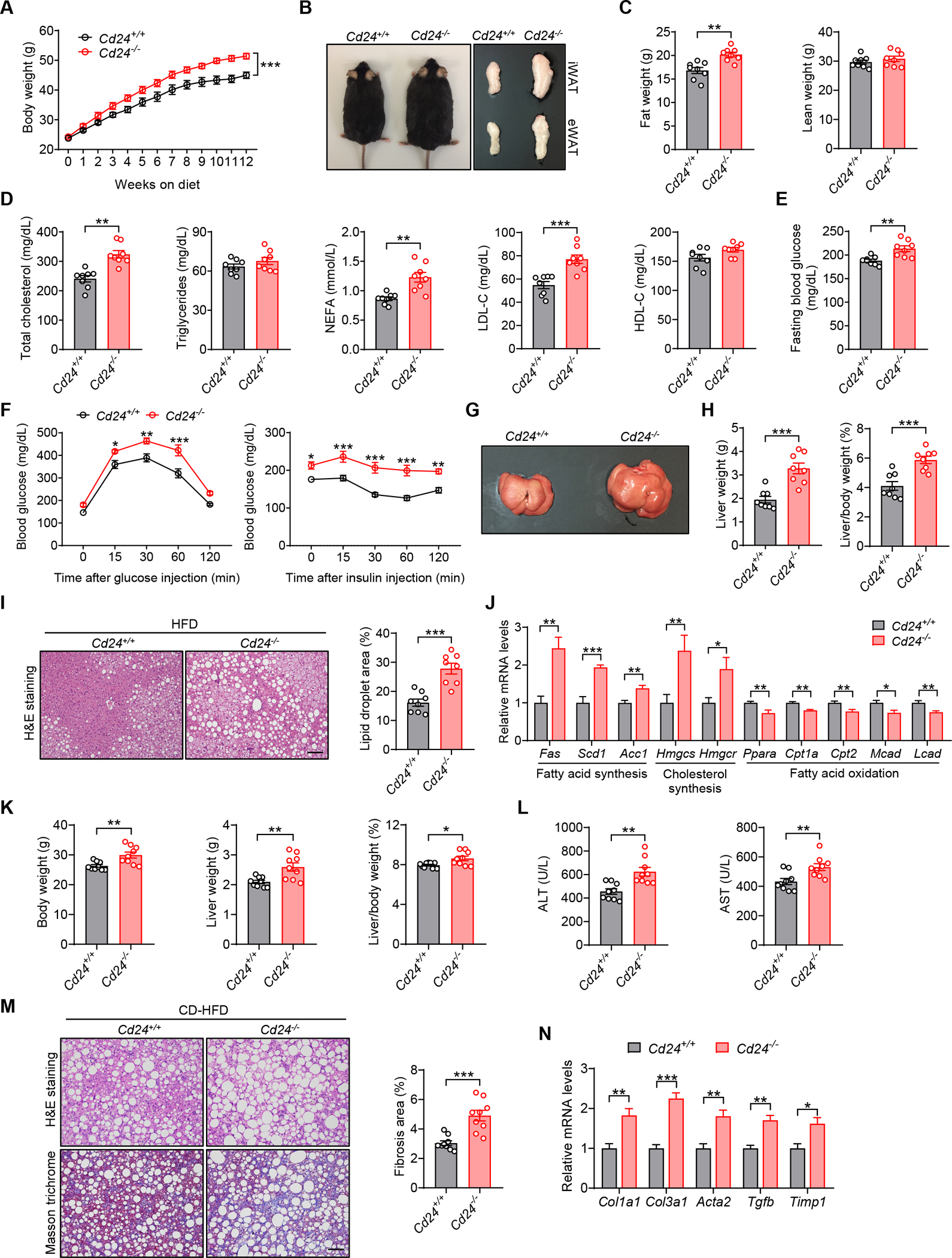
(A-J) Cd24−/− mice and WT littermates were fed a HFD for 12 weeks.
(A) Body weight of mice in the indicated groups. n = 8 per group.
(B) Representative photographs, inguinal and epididymal fat pads of mice in the indicated groups.
(C) Body composition of mice was detected by DEXA. n = 8 per group.
(D) TC, TG, FFA, LDL-C and HDL-C levels of mice in the indicated groups. n = 8 per group.
(E) Fasting blood glucose levels of mice in the indicated groups. n = 8 per group.
(F) GTT and ITT results of mice in the indicated groups. n = 8 per group.
(G) Representative photographs of livers from mice in the indicated groups.
(H) Liver weight and liver/body weight ratio of mice in the indicated groups. n = 8 per group.
(I) Representative images of H&E staining of liver sections. Scale bar, 100 μm. Graph shows the quantitation of lipid droplet area. n = 8 per group.
(J) Relative mRNA levels of key metabolic genes in the livers of mice in the indicated groups. n = 6 per group.
(K-N) Cd24−/− mice and littermate controls were fed a CD-HFD for 12 weeks.
(K) Body weight, liver weight and liver/body weight ratio of mice in the indicated groups. n = 9 per group.
(L) Serum levels of ALT and AST of mice in the indicated groups. n = 9 per group.
(M) H&E and Masson’s trichrome staining of liver sections. Scale bar, 100 μm. Graph shows the quantitation of liver fibrosis area. n = 9 per group.
(N) Relative mRNA levels of profibrotic genes in the livers of mice in the indicated groups. n = 6 per group.
Data are mean ± SEM and representative of two or three independent experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, unpaired Student’s t-test (C-E, H-N), two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (A, F). See also Figure S1.
