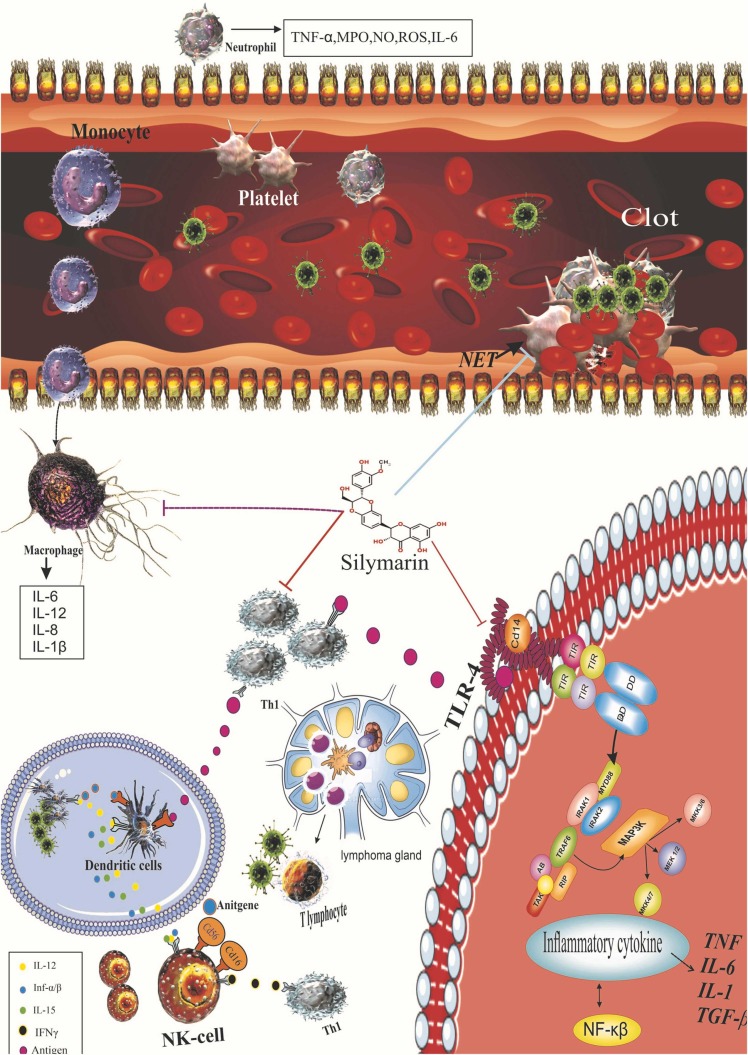
Fig. 3.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative stress effects of silymarin. Sallymarin increases the transcriptional activity of Nrf2. Regulation of the expression of antioxidant genes is critical for controlling oxidative stress and maintaining physiological homeostasis. Of the various regulatory pathways, the Keap1-Cul3-Rbx1, Antioxidants axis is the most important regulator of Nrf2 activity. Sallymarin also reduces the expression of the TLR-4 pathway, which leads to a decrease in NF-KB activity and the production of inflammatory mediators. Silymarin also modulates the immune response, leading to the production of NETS by noutrophil and reducing the overproduction of inflammatory and oxidative factors by immune responses. Anti-inflammatory effects of silymarin. TLR, Toll-like receptor; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; IkB, inhibitor of kappa B; PUSFA, polyunsaturated fatty acids; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; IFNs, interferons; IL, interleukin.