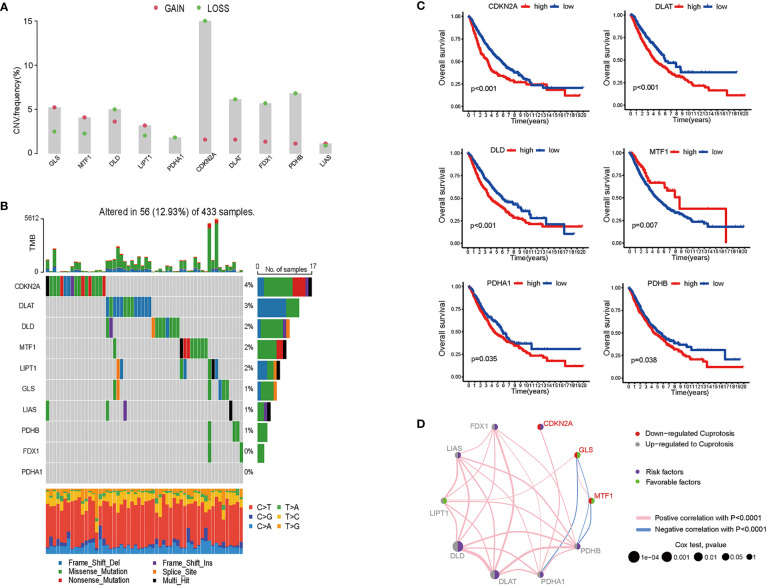
Figure 1.
Genomics and transcriptomics-based bioinformatic analysis on cuproptosis-related genes in lung adenocarcinoma. (A) CNV frequencies showed the loss and gain of ten cuproptosis biomarkers. (B) TMB of cuproptosis biomarkers and the proportion of base-pair alterations in LUAD samples. (For exmale, C>T: cytidine being replaced by adenosine, and so on in a similar fashion.) (C) ROC curves showed overall survival of single cuproptosis-related gene expression in LUAD patients. (D) Association between cuproptosis biomarkers expression and LUAD risks. (For example, DLD was up-regulated in LUAD samples; DLD expression was a risk factor for LUAD patients; and DLD expression was positively correlated with LIPT1, LIAS, FDX1, PDHB, PDHA1, and DLAT).