Figure 2.
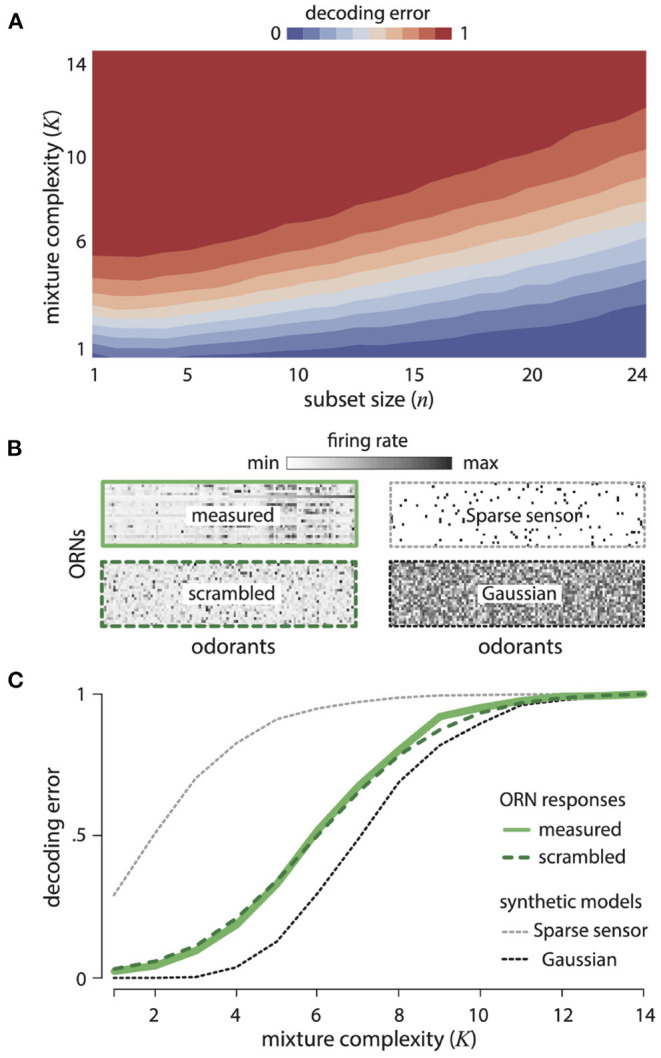
Disordered sensing by ORNs enables accurate decoding of complex mixtures. (A) Error in decoding mixture composition from subsets of ORN responses, as a function of mixture complexity K (i.e., number of mixture components) and ORN subset size n. Results are averaged over 500 odor mixtures of a given complexity, and 50 subsets of a given size. (B) Response matrices for Drosophila ORNs (measured and scrambled), sparse-sensor and Gaussian models (see text for details). (C) Error in decoding complex mixtures from 24 ORNs as a function of mixture complexity K, shown for ORN responses (solid green), a scrambled version of ORN responses (dashed green), and two idealized models (the Gaussian random model, dashed black, and the sparse-sensor model, dashed gray). Results are averaged over 500 odor mixtures of a given complexity. Results from scrambled, Gaussian, and sparse-sensor models are additionally averaged over 100 model instantiations.
