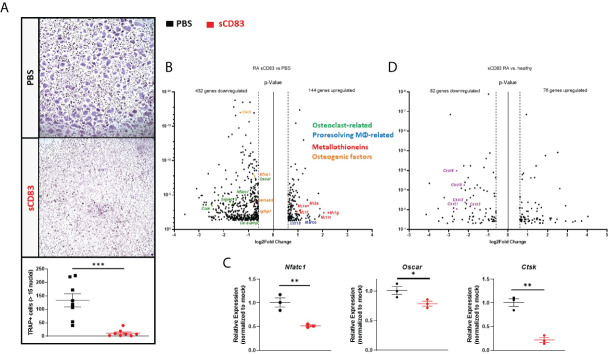
Figure 4.
sCD83 potently suppressed the pro-osteoclastogenic phenotype of CD14+ cells derived from rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. (A) Representative images (A; upper side) used for the quantification of large multinucleated TRAP+ cells with more than 15 nuclei (A; lower side) with n = 8. (B) Volcano plot of RNA sequencing analyses of sCD83- vs. phosphate-buffered saline(PBS)-treated osteoclast cultures generated from CD14+ cells of RA patients on day 7 from three independent samples per condition. The dots depicted on the right-hand side of the log2fold change 0 value represent significantly upregulated transcripts, while the dots on the left-hand side represent significantly downregulated transcripts with log2FC ≥0.6, respectively. Specific dot colors classify the transcripts into characteristic groups: green = osteoclast-related, blue = transcripts associated with alternatively activated M2-like MΦ, red = metallothioneins, and orange = transcripts which are associated with osteoblast formation. (C) Verification of the RNA sequencing data by RT-PCR analyses regarding the expression of osteoclast-related transcripts from one representative experiment (n = 3). (D) Volcano plot of RNA sequencing analysis of sCD83-treated osteoclast cultures derived from RA patients compared to sCD83-treated cultures from healthy donors on day 7 from three independent samples per condition. The dots depicted on the right-hand side of the log2FC 0 value represent significantly upregulated genes, while the dots on the left-hand side represent significantly downregulated genes with log2FC ≥0.6, respectively. The purple dots highlight transcripts of the CXCL-family. (A) Mann–Whitney test and (C) Student’s t-test.